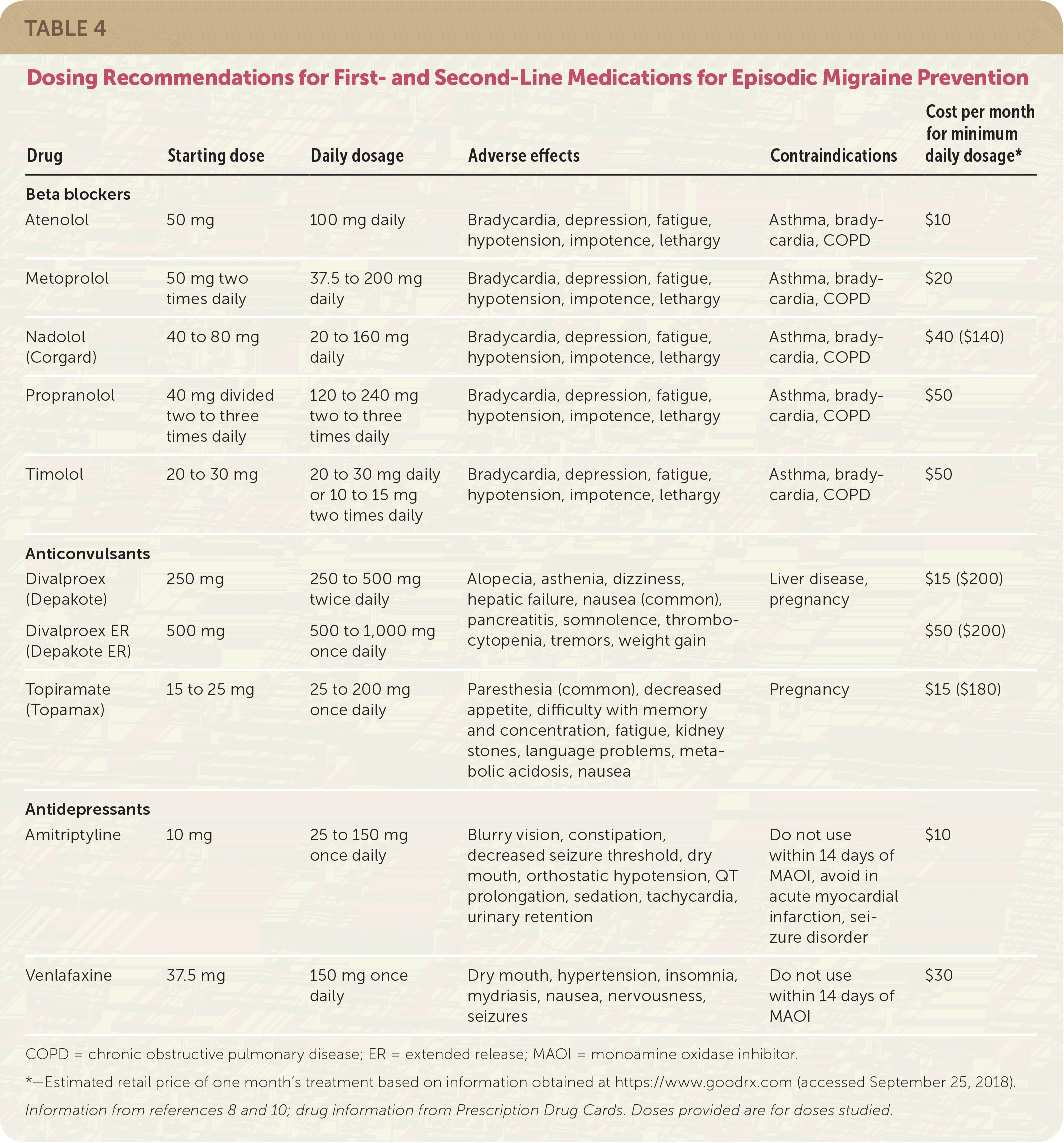
Propranolol’s migraine prevention dosage typically starts at 40mg twice daily. Your doctor may adjust this based on your response and tolerance. Some individuals find relief at lower doses, while others may require up to 160mg daily, divided into two or more doses.
Remember, gradual increase is key. Don’t jump to higher doses immediately. Monitor for side effects like fatigue, low blood pressure, or nausea. Report any concerns to your healthcare provider. They will guide you toward finding the most effective and safest dose for your individual needs.
Important Note: This information is for guidance only and doesn’t substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication, including propranolol. They will consider your medical history and other medications to determine the appropriate dosage and treatment plan for you.
Specific dosage adjustments might be necessary if you have other health conditions like heart problems or liver issues. Your physician will tailor your treatment to account for these factors. Open communication with your doctor ensures the best outcome.
- Propranolol for Migraines: A Dosage Guide
- Understanding Propranolol’s Role in Migraine Prevention
- Standard Propranolol Dosage for Migraine Prevention
- Typical Starting Dosage
- Dosage Increase
- Important Considerations
- Alternative Dosage Schedules
- Monitoring and Adjustment
- Disclaimer:
- Adjusting Propranolol Dosage Based on Individual Needs
- Potential Side Effects of Propranolol and Dosage Considerations
- Dosage Adjustments
- Important Note on Interactions
- Interactions with Other Medications and Propranolol Dosage
- Consulting Your Doctor: Importance of Personalized Dosage Regimen
- Factors Influencing Dosage
- Adjusting Your Propranolol Regimen
Propranolol for Migraines: A Dosage Guide
Your doctor will determine the best Propranolol dosage for your migraines. Typical starting doses range from 10 to 40 mg daily, often divided into two doses. This is a low dose, primarily for migraine prevention, not acute treatment.
Gradual increases may occur if needed, but rarely exceed 160 mg per day. Your doctor will closely monitor your response and adjust accordingly. Always follow your doctor’s instructions exactly.
Dosage adjustments depend on your individual response and potential side effects. Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and nausea. Report any side effects immediately.
For optimal results, take Propranolol consistently as prescribed. Skipping doses can reduce its effectiveness in preventing migraines. Never abruptly stop taking Propranolol without consulting your doctor.
Remember, this information is for general guidance only. It does not substitute for personalized advice from your healthcare provider. They will consider your medical history and other factors to create a tailored treatment plan.
Understanding Propranolol’s Role in Migraine Prevention
Propranolol, a beta-blocker, doesn’t treat acute migraines; it prevents them. It works by reducing the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, which plays a role in triggering migraines for many individuals. This action helps stabilize blood vessels and reduces the frequency and severity of attacks.
Doctors typically prescribe propranolol for migraine prevention when lifestyle changes and over-the-counter pain relievers haven’t provided sufficient relief. It’s particularly helpful for those experiencing frequent migraines, perhaps more than two per month.
| Factor | Impact on Propranolol’s Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Migraine Frequency | More effective for frequent migraines. |
| Individual Response | Response varies; some experience significant reduction, others minimal effect. |
| Combination Therapy | Often used alongside other preventative medications. |
| Dosage Adjustment | Dosage may need adjustment based on individual response and tolerance. |
Remember, propranolol has potential side effects. Common ones include fatigue, dizziness, and nausea. These side effects usually subside as your body adjusts. Always discuss potential side effects and drug interactions with your doctor before starting propranolol or any medication.
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage for you based on your individual health profile and migraine history. They will closely monitor your progress and make adjustments as needed to optimize treatment and minimize side effects. Regular check-ups are vital to ensure safe and effective use.
Standard Propranolol Dosage for Migraine Prevention
Typically, propranolol for migraine prevention starts with a low dose and gradually increases as needed. Your doctor will personalize your dosage based on your individual response and medical history.
Typical Starting Dosage
A common starting dose is 10-20 mg twice daily.
Dosage Increase
If your migraines persist, your doctor might increase the dosage gradually, possibly to a maximum of 160 mg per day, divided into two or four doses. Increases are usually made in small increments, with careful monitoring of your response and side effects.
Important Considerations
- Individual Response: Everyone reacts differently to medication. What works for one person may not work for another.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and nausea. Report any concerning side effects to your doctor immediately.
- Other Medications: Propranolol can interact with other medications. Be sure to inform your doctor of all medications you are currently taking.
- Medical History: Pre-existing conditions such as heart problems or asthma must be carefully considered when prescribing propranolol.
Alternative Dosage Schedules
Some patients might find success with different dosing schedules, such as a single larger dose in the morning or a modified schedule based on personal needs and response.
Monitoring and Adjustment
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are necessary to monitor your progress, adjust the dosage as needed, and manage potential side effects. The goal is to find the lowest effective dose that provides sufficient migraine relief.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with your doctor before starting any new medication, including propranolol, to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure its suitability for your individual circumstances.
Adjusting Propranolol Dosage Based on Individual Needs
Your doctor will determine the appropriate starting dose of propranolol for your migraines, usually beginning with a low dose and gradually increasing it as needed. Common starting dosages range from 10mg to 40mg, taken twice daily. This gradual approach allows for close monitoring of your response and minimizes side effects.
Dosage adjustments are based on several factors. These include the severity and frequency of your migraines, your overall health, and your response to the medication. If you experience significant migraine relief at a lower dose, there’s no need to increase it. Conversely, if your migraines persist despite taking the prescribed dose, your doctor may cautiously increase it in small increments, perhaps by 10mg or 20mg every few days or weeks.
Regular monitoring is crucial. Report any side effects, such as fatigue, dizziness, or low blood pressure, immediately to your doctor. These side effects might necessitate a dosage reduction or a change in medication. Remember, finding the optimal dose is an iterative process. It involves careful observation, open communication with your physician, and a willingness to adjust the treatment plan accordingly.
Maximum daily dosages of propranolol for migraine prevention generally do not exceed 240mg, but this varies based on individual tolerance and your doctor’s assessment. Always follow your physician’s instructions carefully and never adjust your dosage without their explicit guidance. Consistent communication with your doctor is key to safe and effective migraine management.
Potential Side Effects of Propranolol and Dosage Considerations
Propranolol, while effective for migraine prevention, can cause side effects. Common ones include fatigue, dizziness, nausea, and cold hands and feet. Less frequent, but still possible, are sleep disturbances, depression, and bronchospasm (especially in those with asthma or similar conditions). Always inform your doctor about your medical history, including any respiratory issues or allergies.
Dosage Adjustments
Starting doses for migraine prophylaxis typically range from 10mg to 40mg twice daily. Your doctor will adjust your dosage based on your response and tolerance. They might increase the dose gradually, carefully monitoring for side effects. If you experience significant side effects, discuss them immediately with your physician. Dosage reduction or alternative treatments may be necessary. Regular monitoring is key for optimal results and minimizing potential problems.
Important Note on Interactions
Propranolol can interact with other medications. Be sure to disclose all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking to your doctor. This includes over-the-counter drugs. This ensures your safety and the effectiveness of your treatment plan.
Interactions with Other Medications and Propranolol Dosage
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Propranolol’s effects can be altered, and its safety profile can change, depending on what else you’re using.
Here are some key interactions to discuss with your healthcare provider:
- Insulin and oral hypoglycemics: Propranolol can mask the symptoms of low blood sugar. Your doctor may need to adjust your diabetes medication dosage.
- Calcium channel blockers (like verapamil and diltiazem): Combining these can significantly lower your heart rate and blood pressure, potentially causing dangerous side effects. Careful monitoring is required.
- MAO inhibitors: Concurrent use can cause dangerously low blood pressure. A significant time gap between taking these medications is usually necessary.
- Beta-agonists (like albuterol): Propranolol blocks the effects of these, counteracting their bronchodilating action. This is particularly problematic for people with asthma.
- Tricyclic antidepressants (like amitriptyline): Using both may increase the risk of low blood pressure and other cardiovascular effects.
Adjusting your propranolol dosage might be necessary depending on these interactions. Your doctor will help you determine the safest and most effective approach. Regular blood pressure and heart rate monitoring are often recommended when taking propranolol, especially when other medications are involved.
This list is not exhaustive. Discuss all your medications with your physician before starting propranolol to minimize potential risks and ensure optimal migraine management.
- Never adjust your propranolol dose without consulting your doctor.
- Report any new or worsening symptoms immediately.
- Maintain open communication with your doctor about your treatment plan.
Consulting Your Doctor: Importance of Personalized Dosage Regimen
Always discuss your migraine treatment with your doctor. They will consider your specific medical history, including other medications you take, any pre-existing conditions, and your response to previous treatments. This information helps determine the right starting dose of propranolol for you. The initial dose might be low, gradually increasing until your migraines are effectively managed or side effects become problematic. Your doctor might start with 10-40mg twice daily, adjusting based on your needs and tolerance.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Several factors influence your propranolol dosage. Your age, weight, and overall health play a significant role. If you have liver or kidney problems, the dosage may need adjustment to avoid potential complications. Your doctor will closely monitor your blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital signs throughout the treatment. Regular checkups allow them to make necessary adjustments, ensuring your safety and treatment efficacy.
Adjusting Your Propranolol Regimen
Never alter your propranolol dosage without consulting your doctor. Suddenly stopping or changing your dose can lead to withdrawal symptoms or worsen your migraines. Open communication with your doctor is vital. Report any side effects you experience, such as dizziness, fatigue, or nausea, so they can make necessary adjustments to your dosage or treatment plan. Remember, a personalized approach ensures optimal migraine management with minimal risk. This involves ongoing monitoring and open communication between you and your healthcare provider.