Yes, 10 mg of prednisone is generally considered a lower dosage, particularly when compared to initial doses often prescribed for conditions like severe inflammation or autoimmune diseases. Many treatment plans begin with significantly higher daily doses, gradually tapering down over time.
However, “lower” is relative. A 10mg dose might be a maintenance dose following a higher initial treatment, or it could be a starting point for less severe conditions. Your individual needs and the specific condition being treated directly influence what constitutes a low dose. Factors like your weight, overall health, and response to the medication are crucial in determining the appropriate dosage.
Always discuss your prednisone dosage with your doctor. They can assess your situation, considering your medical history and current health status, to determine the optimal and safest dosage for you. Never adjust your prednisone dosage without your physician’s explicit guidance; doing so may compromise your treatment and potentially lead to adverse effects.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Consult your doctor before making any changes to your medication regimen.
- Is 10mg Prednisone a Low Dosage?
- Factors Affecting Prednisone Dosage
- Seeking Professional Guidance
- Prednisone Dosage: A General Overview
- Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage
- Common Prednisone Dosage Regimens
- Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage Needs
- 10mg Prednisone: Common Uses and Considerations
- Potential Side Effects at 10mg Prednisone
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Other Potential Side Effects
- When to Consult a Doctor About Your Prednisone Dosage
- Dosage Adjustments & Side Effects
- Long-Term Prednisone Use
Is 10mg Prednisone a Low Dosage?
Whether 10mg of prednisone is a low dosage depends entirely on the individual and their specific condition. For some, it might be considered a low dose, particularly if they’re using it for mild inflammation. Others, however, may find this dose quite significant, especially if they have a pre-existing condition or are sensitive to the medication. The prescribed dosage is always tailored to the patient’s needs. Factors influencing the prescription include the severity of the illness, the patient’s age, weight, and overall health.
Factors Affecting Prednisone Dosage
Your doctor considers several elements when determining the appropriate prednisone dosage. These include the specific medical condition being treated, the patient’s response to the drug, and potential side effects. For example, a low dose might be sufficient for allergic reactions, whereas higher doses are frequently needed for autoimmune disorders. Regular blood tests are often used to monitor the body’s response and adjust the dosage accordingly to maximize effectiveness and minimize side effects. Always discuss any concerns about your prednisone dosage with your physician. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure you receive the most appropriate treatment plan.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Ultimately, only your doctor can determine if 10mg of prednisone is a low dose for your particular circumstances. They’ll base this decision on your unique medical history and current health status. Never adjust your prednisone dosage without explicit medical advice; doing so can have serious health consequences. Open communication with your healthcare provider ensures optimal treatment and patient safety.
Prednisone Dosage: A General Overview
Prednisone dosage depends entirely on your specific condition and individual response. Your doctor determines the appropriate dose, and it’s crucial to follow their instructions precisely.
Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage
- Severity of your condition: More severe conditions often require higher initial doses.
- Your body weight: Dosage is often adjusted based on your weight.
- Your overall health: Existing health problems can influence the dosage.
- Your response to treatment: The dose may be adjusted based on how your body reacts to the medication.
Typical starting doses range from 5mg to 60mg daily, though higher doses might be used for specific situations in the short term. Long-term use usually involves significantly lower doses. Your doctor will gradually reduce the dosage as your condition improves, to minimize side effects.
Common Prednisone Dosage Regimens
- Short-term treatment (e.g., inflammation): Higher doses for a short period (days to weeks).
- Long-term treatment (e.g., autoimmune disorders): Lower doses for an extended period (months to years), often with gradual tapering.
- Alternate-day therapy: Taking the entire dose every other day can reduce side effects.
Remember, this is general information only. Never adjust your prednisone dosage without your doctor’s explicit guidance. Always discuss any concerns or side effects with your healthcare provider. They will monitor your progress and make adjustments to your medication as needed.
Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage Needs
Your doctor determines your prednisone dosage based on several key factors. The severity of your condition plays a major role; more severe conditions generally require higher doses. For example, someone with a severe autoimmune disease might need a much higher dose than someone with mild allergic reactions.
Your individual response to the medication also matters. Some people respond well to lower doses, while others require higher amounts to achieve the same effect. Regular monitoring of your condition and blood work helps your doctor adjust the dosage appropriately.
Your age and overall health significantly influence dosage. Children, older adults, and those with pre-existing health conditions often require lower doses or more careful monitoring due to increased risk of side effects.
Other medications you’re taking can interact with prednisone, potentially requiring dosage adjustments. Inform your doctor about all your medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Finally, the specific condition being treated directly impacts the dose. Different conditions respond differently to prednisone, necessitating varied dosage regimens.
| Factor | Impact on Dosage |
|---|---|
| Severity of Condition | Higher dose for severe conditions |
| Individual Response | Dosage adjusted based on patient’s response |
| Age and Overall Health | Lower doses often needed for children, older adults, and those with other health issues |
| Drug Interactions | Dosage may need adjustment based on other medications |
| Specific Condition | Dosage varies depending on the condition being treated |
10mg Prednisone: Common Uses and Considerations
Ten milligrams of prednisone is frequently prescribed for managing various inflammatory conditions. Common uses include treating allergic reactions, such as severe asthma exacerbations or allergic rhinitis requiring rapid symptom relief. It also finds application in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease, helping to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms. Doctors may also use a 10mg dose for managing certain skin conditions, like severe eczema or psoriasis, and for reducing swelling after organ transplantation.
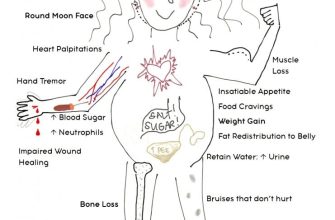
However, remember prednisone carries potential side effects. Long-term use, even at low doses, can increase the risk of osteoporosis, high blood pressure, and increased blood sugar. Weight gain and mood changes are also possibilities. Your doctor will carefully monitor you for these effects, adjusting the dosage or duration of treatment as needed. Always inform your physician about all other medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential interactions.
Tapering off prednisone is crucial to prevent withdrawal symptoms, which can include fatigue, muscle weakness, and joint pain. Your doctor will create a gradual tapering schedule tailored to your individual needs. Never stop prednisone abruptly without consulting your healthcare provider. Adherence to your physician’s instructions is paramount for achieving optimal results and minimizing potential risks.
Before starting prednisone, discuss your medical history with your doctor, specifically mentioning any existing heart, liver, or kidney problems, diabetes, glaucoma, or infections. This information helps them assess the risks and benefits of prednisone for your specific situation. Regular monitoring, including blood tests, may be necessary to check for side effects and ensure the effectiveness of treatment.
Potential Side Effects at 10mg Prednisone
While 10mg is considered a relatively low dose of prednisone, side effects are still possible. Commonly reported effects at this dosage include mild insomnia, increased appetite leading to weight gain, and mood changes such as irritability or anxiety. Some individuals experience mild fluid retention, causing swelling in the ankles or face.
Gastrointestinal Issues
At 10mg, you might notice some upset stomach or heartburn. Rarely, more serious gastrointestinal problems can occur, such as ulcers. If you experience persistent stomach pain or vomiting, contact your doctor immediately.
Other Potential Side Effects
Less frequent side effects at this dosage include increased blood sugar levels, potentially worsening existing diabetes, and increased blood pressure. Muscle weakness or thinning of the skin are also possibilities, though less likely at 10mg. It’s crucial to monitor your blood pressure and blood sugar regularly if you’re prescribed this medication.
Remember, individual responses to medication vary. This information provides a general overview; always discuss any concerns with your prescribing physician. They can assess your specific risk factors and provide personalized advice.
When to Consult a Doctor About Your Prednisone Dosage
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following: severe abdominal pain, unexplained weight gain exceeding 2 pounds in a week, muscle weakness or loss of coordination, increased thirst or urination, blurred vision, easy bruising or bleeding, facial swelling (moon face), persistent or worsening headaches, trouble sleeping, worsening of your existing condition, or new symptoms not previously discussed.
Dosage Adjustments & Side Effects
Schedule a doctor’s appointment to discuss potential dosage adjustments if your symptoms aren’t improving after a reasonable timeframe, usually within a few weeks. Similarly, if side effects are significantly impacting your quality of life, even if minor, a discussion with your doctor is needed. They can help you manage side effects or consider alternatives. Don’t hesitate to call if you have concerns about potential side effects, however mild they may seem.
Long-Term Prednisone Use
Long-term prednisone use (over three weeks) requires close medical supervision. Regular check-ups are crucial to monitor your overall health and address any potential complications. Your doctor will likely adjust your dosage gradually to minimize withdrawal effects and prevent rebound flares of your underlying condition. This gradual tapering process is vital.