Prednisone significantly weakens your immune system, increasing your susceptibility to fungal infections. This heightened risk applies to various fungal species, including Candida, Aspergillus, and Pneumocystis. Understanding this connection is key to proactive health management.
Monitor for common fungal infection symptoms like skin rashes, mouth sores (thrush), cough, shortness of breath, or fever. Early detection is paramount. Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of these, especially if you are on prednisone. A prompt diagnosis and treatment plan are vital for preventing complications.
Prophylactic antifungal medications might be necessary, especially for individuals with known risk factors or those requiring long-term prednisone therapy. Discuss this preventative measure with your physician; they can assess your individual needs and determine the best course of action. Remember, open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for managing potential risks.
Beyond medication, maintaining good hygiene practices such as handwashing and oral hygiene helps minimize your risk of fungal infections. A balanced diet also supports a robust immune system, mitigating the effects of prednisone-induced immunosuppression. This holistic approach complements medical interventions for better overall health.
- Fungal Infection with Prednisone: A Detailed Guide
- Preventing Fungal Infections While on Prednisone
- Treating Fungal Infections on Prednisone
- Specific Considerations
- Increased Risk of Fungal Infections While on Prednisone
- Common Types of Fungal Infections Associated with Prednisone Use
- Preventing Fungal Infections While Taking Prednisone
- Dietary Considerations
- Treatment and Management of Fungal Infections in Prednisone Users
Fungal Infection with Prednisone: A Detailed Guide
Prednisone, while effective for managing inflammation, weakens your immune system, increasing your susceptibility to fungal infections. Common culprits include Candida (causing thrush or yeast infections) and Aspergillus (potentially leading to serious lung infections). Recognize symptoms promptly: skin rashes, persistent cough, shortness of breath, or white patches in your mouth or throat warrant immediate medical attention.
Preventing Fungal Infections While on Prednisone
Maintain excellent hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, shower daily, and keep your skin dry. Avoid contact with individuals suffering from fungal infections. Consume yogurt with live cultures – probiotics can support gut health and help prevent Candida overgrowth. Inform your doctor about any history of fungal infections before starting prednisone. Discuss prophylactic antifungal medication if your risk is high.
Treating Fungal Infections on Prednisone
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection. Your doctor will prescribe antifungal medications – oral or topical, depending on the location and extent of the infection. They may adjust your prednisone dosage or consider alternative treatments if possible. Complete the full course of prescribed medication, even if symptoms improve, to prevent recurrence. Closely monitor your condition and report any worsening symptoms or lack of improvement immediately.
Specific Considerations
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or undergoing chemotherapy, are particularly vulnerable. These individuals require closer monitoring and may need more aggressive preventative measures. Always communicate openly with your healthcare provider about any concerns related to fungal infections while on prednisone. They are your best resource for tailored guidance and support.
Increased Risk of Fungal Infections While on Prednisone
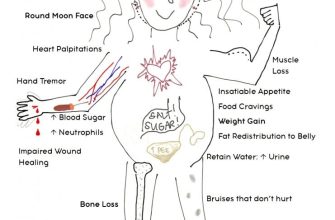
Prednisone weakens your immune system, making you more susceptible to fungal infections. This increased vulnerability stems from prednisone’s suppression of your body’s natural defenses against fungi.
Common fungal infections appearing during prednisone use include oral thrush (candidiasis), skin infections, and, in severe cases, invasive fungal infections affecting internal organs. These infections can range in severity from mild discomfort to life-threatening complications.
Be vigilant about any unusual skin rashes, oral lesions (sores in the mouth), or persistent coughing. Early detection is key to quicker treatment and a better outcome. Report any new symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Your doctor might suggest preventative measures like antifungal mouthwash if you are at high risk of oral thrush. They will carefully weigh the benefits of prednisone against potential risks, and may explore alternative treatments if possible.
Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing and avoiding contact with individuals experiencing fungal infections, can also help minimize your risk. A balanced diet supporting a healthy immune system is also beneficial.
Remember, open communication with your doctor is critical. They can assess your individual risk, monitor your condition, and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Common Types of Fungal Infections Associated with Prednisone Use
Prednisone, while beneficial for many conditions, weakens the immune system, increasing susceptibility to fungal infections. Understanding these infections is key to prompt treatment.
- Candidiasis: This yeast infection commonly affects the mouth (thrush), esophagus, vagina, and skin. Look for white patches, redness, or soreness. Treatment usually involves antifungal medications like fluconazole or nystatin.
- Aspergillosis: Aspergillus fungus can cause lung infections (aspergillosis) particularly in individuals with weakened immunity. Symptoms mimic other respiratory illnesses, but can progress to severe lung damage. Diagnosis requires chest imaging and lab tests; treatment involves antifungal drugs like voriconazole or amphotericin B. Early detection is crucial.
- Histoplasmosis: This fungal infection usually affects the lungs, but it can spread to other organs. Exposure to bird or bat droppings carries risk. Symptoms vary; diagnosis involves blood tests and imaging. It’s treated with itraconazole or amphotericin B.
- Coccidioidomycosis: Inhalation of Coccidioides spores, found in specific geographic areas (e.g., southwestern US), leads to this infection. Symptoms resemble flu or pneumonia; severe cases may require antifungal therapy (fluconazole or amphotericin B).
- Cryptococcosis: Cryptococcus fungus primarily affects the lungs and central nervous system. Immunocompromised individuals are at higher risk. Diagnosis involves cerebrospinal fluid analysis and cultures; treatment requires antifungal agents like fluconazole or amphotericin B.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a fungal infection while taking prednisone. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital for positive outcomes.
Preventing Fungal Infections While Taking Prednisone
Maintain meticulous hygiene. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after touching public surfaces or before meals. Shower daily, paying close attention to skin folds and areas prone to moisture. Keep your nails trimmed and clean to prevent fungal growth underneath.
Dietary Considerations
Boost your immune system with a nutrient-rich diet. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates, as these can weaken your immune response. Probiotics, found in yogurt and fermented foods, may also help maintain gut health, which impacts immunity.
Avoid sharing personal items. This includes towels, razors, and clothing. These items can easily harbor fungi and lead to cross-contamination. Use clean, fresh towels after showering and avoid wearing damp clothes for extended periods.
Recognize and treat any minor skin irritations immediately. Small cuts, scrapes, or rashes can provide entry points for fungal infections. Cleanse these areas thoroughly and apply appropriate topical treatments as needed. If they worsen, consult a doctor.
Promptly address any signs of a fungal infection. Watch for changes in your skin, such as redness, itching, or unusual rashes. Seek medical attention if you suspect a fungal infection so treatment can begin as soon as possible. Early intervention prevents widespread infections.
Treatment and Management of Fungal Infections in Prednisone Users
Prompt diagnosis is key. Your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and may order tests like cultures or biopsies to identify the specific fungus and guide treatment.
Treatment usually involves antifungal medication. The choice of medication depends on the type of fungus and the severity of the infection. Oral antifungals, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, are common choices. For severe infections, intravenous antifungal therapy might be necessary.
Duration of treatment varies, often lasting several weeks or even months, depending on the infection’s response. Close monitoring by your physician is crucial to ensure the infection clears completely.
Managing your prednisone dose is also important. While prednisone reduces inflammation, it can suppress your immune system, increasing your susceptibility to fungal infections. Your doctor may adjust your prednisone dosage to strike a balance between managing your underlying condition and minimizing your risk of infection. This may involve a gradual reduction if possible.
Maintaining good hygiene practices is vital to prevent future fungal infections. This includes thoroughly drying your skin after showering, avoiding prolonged skin exposure to moisture, and practicing good hand hygiene.
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor allow for ongoing monitoring of your infection and your response to treatment. This helps ensure early detection of any complications or relapse. Report any new or worsening symptoms immediately.
For specific advice tailored to your individual circumstances, always consult your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional. Self-treating can be risky and potentially harmful.