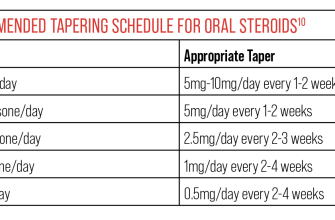
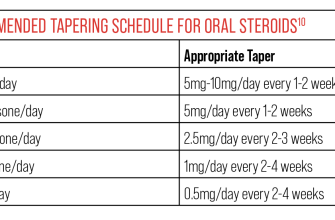
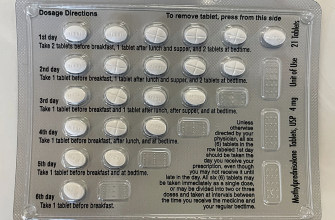
Begin tapering prednisone slowly, usually at a rate of 2.5-5 mg every 3-7 days. This gradual reduction minimizes withdrawal symptoms. A specific schedule will depend on your individual needs and your doctor’s assessment of your condition.
For example, a 20mg daily dose might be reduced to 17.5mg for a week, then 15mg the following week, and so on. Always follow your physician’s instructions meticulously. They will tailor a tapering schedule based on factors like your initial dose, the duration of your prednisone use, and your overall health.
Consider alternative therapies, such as transitioning to an immunosuppressant medication or increasing other treatments during the tapering process. This can help manage underlying conditions while your body adjusts to lower prednisone levels. Discuss these options with your doctor to find the best strategy for your situation.
Remember: Monitor yourself closely for signs of withdrawal like fatigue, joint pain, and nausea. Report any concerning symptoms immediately to your healthcare provider. Regular communication with your doctor throughout the tapering process is key to a successful outcome and prevents complications.
- Examples of Prednisone Tapers
- Example 1: Moderate-Dose Taper (for conditions like moderate asthma or inflammatory arthritis)
- Example 2: Slow Taper for Long-Term Use (for conditions like lupus or severe autoimmune diseases)
- Prednisone Taper Schedule for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Prednisone Taper for Allergic Reactions
- Short-Term Prednisone Taper for Asthma Exacerbation
- Prednisone Taper for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Important Considerations When Tapering Prednisone
- Monitoring Your Body’s Response
- Managing Potential Side Effects
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- Medication Interactions
- Individualized Approach
Examples of Prednisone Tapers
Prednisone tapering schedules vary greatly depending on individual needs and the underlying condition. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions. These examples illustrate common approaches, but they are not a substitute for medical advice.
Example 1: Moderate-Dose Taper (for conditions like moderate asthma or inflammatory arthritis)
- Start at 40mg daily.
- Reduce by 5mg every 3-5 days.
- Once at 10mg, reduce by 2.5mg every 3-5 days.
- Continue decreasing until you reach 0mg.
This schedule might take 4-6 weeks. Monitor for symptoms; slower reduction may be needed if you experience flare-ups.
Example 2: Slow Taper for Long-Term Use (for conditions like lupus or severe autoimmune diseases)
- Start at a higher dose (this is determined by your physician).
- Reduce by 1-2.5mg every 1-2 weeks.
- Progress to even smaller decrements (e.g., 1mg) as the dose decreases.
- Expect a longer taper, potentially several months or longer.
This approach minimizes the risk of withdrawal symptoms and allows for careful monitoring of the condition.
Example 3: Rapid Taper (rarely used; only under close medical supervision)
In rare instances, a more rapid taper may be considered, but it involves greater risk of rebound inflammation. This should only occur under strict physician guidance and frequent monitoring.
Important Note: These are just examples. Your doctor will personalize your taper based on your specific health, medication history, and response to treatment. Always discuss any concerns or changes in your condition with your healthcare provider.
Prednisone Taper Schedule for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Your doctor will personalize your prednisone taper based on your specific condition and response to treatment. However, a common approach involves slow reductions to minimize withdrawal symptoms. A typical schedule might start with a daily dose reduction of 5-10mg every 3-7 days. For example, if you’re on 60mg daily, you might reduce to 55mg for a week, then 50mg, and so on. This gradual decrease continues until the prednisone is completely discontinued.
For instance, a patient on 40mg daily might follow this example: 40mg for 1 week, 35mg for 1 week, 30mg for 1 week, 25mg for 1 week, 20mg for 1 week, 15mg for 1 week, 10mg for 1 week, 5mg for 1 week, and then stop. This is just an example; adjustments are frequently necessary.
Close monitoring is crucial. Your doctor will assess your symptoms, blood work, and overall health to adjust the tapering schedule as needed. They might slow the process if you experience symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, or a flare-up of your IBD. Conversely, they may accelerate the taper if you show significant improvement.
Alternative tapering strategies, such as alternate-day dosing, may be used, particularly in cases of less severe disease. Your gastroenterologist will discuss the optimal approach for your individual needs. Remember, this is not a “one-size-fits-all” plan. Patient-specific factors influence the best tapering schedule.
Always communicate openly with your doctor regarding any changes in your health or concerns about the prednisone taper. Regular check-ups are essential to monitor your progress and make timely adjustments to the plan.
Prednisone Taper for Allergic Reactions
Your doctor will determine the best prednisone taper schedule based on the severity of your allergic reaction and your individual response to treatment. A typical taper might involve a slow decrease in dosage over several weeks. For example, if you’re on 60mg daily, you might reduce by 5-10mg every 3-7 days. Always follow your doctor’s precise instructions.
A common tapering schedule for mild to moderate allergic reactions might look like this:
| Day | Dosage (mg) |
|---|---|
| 1-3 | 60 |
| 4-7 | 50 |
| 8-11 | 40 |
| 12-15 | 30 |
| 16-19 | 20 |
| 20-23 | 10 |
| 24-27 | 5 |
| 28 | 0 |
Note: This is just a sample schedule. Your doctor may adjust the dosage and frequency based on your symptoms and overall health. Rapid tapering can cause withdrawal symptoms, including fatigue, joint pain, and nausea. Always communicate any concerns or side effects to your doctor immediately. They might recommend a slower taper if needed. Monitor your symptoms carefully during the tapering process.
Remember, never stop prednisone abruptly without consulting your physician. Close monitoring allows for adjustments to ensure a safe and effective reduction in your medication.
Short-Term Prednisone Taper for Asthma Exacerbation
A typical short-term prednisone taper for an asthma exacerbation involves a rapid decrease in dosage. For instance, a patient initially prescribed 40mg daily might reduce to 30mg after 3 days, then 20mg after another 3 days, followed by 10mg after a further 3 days, and finally, discontinuation after a week.
Adjustments are crucial. This schedule serves as a guideline. Your doctor will adjust the taper based on your individual response to treatment. Factors such as symptom control, lung function tests (like peak expiratory flow rate), and overall clinical status dictate the speed and specifics of the reduction.
Monitoring is key. Regularly scheduled follow-up appointments allow for assessment of your progress and necessary modifications to the tapering plan. Expect to undergo frequent lung function testing during the taper.
Sudden cessation is generally discouraged. Abruptly stopping prednisone can lead to relapse or adrenal insufficiency. A gradual decrease minimizes these risks, ensuring a smoother transition.
Alternative tapering schedules exist. Some physicians might prefer a slower decline, particularly for patients with severe asthma or a history of complications. Your healthcare provider will explain the best approach for your particular circumstances. Always discuss potential side effects and any concerns you have with your doctor.
Prednisone Taper for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reducing prednisone dosage requires careful planning. Your rheumatologist will personalize your taper based on your specific condition and response to treatment. A typical approach involves gradual decreases, often by 2.5mg or 5mg every 1-2 weeks.
Here’s a sample schedule, but remember: this is not a prescription; consult your doctor:
- Starting Dose (Example): 40mg daily
- Week 1-2: 35mg daily
- Week 3-4: 30mg daily
- Week 5-6: 25mg daily
- Week 7-8: 20mg daily
- Week 9-10: 15mg daily
- Week 11-12: 10mg daily
- Week 13-14: 5mg daily
- Week 15: Stop Prednisone
This is just one example; your doctor may recommend a slower or faster reduction, depending on factors like your disease activity, side effects, and overall health.
- Monitor for flares: Report increased joint pain, swelling, stiffness, or fatigue immediately.
- Adjustments are possible: If you experience a flare, your doctor might slow the tapering process or even temporarily increase the dosage.
- Alternative medications: Your doctor will likely work to establish you on other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or biologics during the taper to manage the rheumatoid arthritis.
- Regular appointments: Consistent monitoring during the taper is crucial. Your doctor will use blood tests and clinical assessments to guide the process.
Successfully weaning off prednisone requires close collaboration with your healthcare provider. Open communication about your symptoms and concerns is vital for a safe and effective taper.
Important Considerations When Tapering Prednisone
Never stop Prednisone abruptly. A sudden cessation can trigger adrenal insufficiency, potentially leading to serious health issues. Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule, usually decreasing the dose gradually over weeks or months. This schedule depends on several factors including the initial dose, the duration of treatment, and your overall health.
Monitoring Your Body’s Response
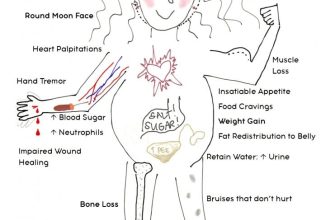
Closely monitor yourself for any signs of adrenal insufficiency during the tapering process. This includes fatigue, weakness, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, dizziness, low blood pressure, and abdominal pain. Report any of these symptoms to your physician immediately. Regular blood tests can also help monitor your cortisol levels.
Managing Potential Side Effects
Prednisone withdrawal can cause various side effects, ranging from mild to severe. These can include joint pain, muscle aches, and mood changes. Your doctor might recommend additional medications to manage these side effects. Maintain open communication with your doctor throughout the tapering process to address any concerns or complications.
Lifestyle Adjustments
While tapering, adopt a healthy lifestyle to support your body’s adaptation. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and prioritizing sufficient sleep. These habits can minimize the severity of withdrawal symptoms and promote overall well-being. Remember that stress can exacerbate withdrawal symptoms, so focus on stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga.
Medication Interactions
Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. Some medications may interact with Prednisone, potentially affecting the tapering process or increasing the risk of side effects. This includes over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Individualized Approach
Each tapering plan is unique. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach. Your doctor will tailor the schedule to your specific needs and medical history. Be patient, follow your doctor’s instructions meticulously, and don’t hesitate to ask questions. Your health is paramount, so active participation in your treatment is key.