Never take prednisone and levofloxacin concurrently without consulting your doctor. This combination may increase your risk of tendon rupture, especially in older adults or those with existing conditions like kidney disease. Your physician will assess your individual health profile and medication history to determine if this combination is appropriate for you.
If your doctor approves this combination, meticulously follow the prescribed dosage and schedule. Report any unusual symptoms, such as pain or swelling in your joints or tendons, immediately. Early detection is key in managing potential complications associated with this drug regimen.
Specific monitoring might be recommended by your doctor, potentially including regular blood tests to check your liver and kidney function. Open communication with your healthcare provider is paramount throughout the treatment. Don’t hesitate to ask questions or express concerns about potential side effects.
Remember that individual responses to medications vary considerably. What works well for one person might not be suitable for another. This guide offers general information; personalized medical advice should always come from a qualified healthcare professional.
- Prednisone and Levofloxacin: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Infection Treatment
- Specific Situations Where Prednisone Might Be Used
- Levofloxacin: Mechanism of Action and Uses
- Potential Drug Interactions Between Prednisone and Levofloxacin
- Common Side Effects When Taking Both Medications
- Specific Patient Considerations and Precautions
- Diabetes Management
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Mental Health Monitoring
- Infections
- Liver and Kidney Function
- Allergies
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Elderly Patients
- Children
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prednisone and Levofloxacin
- Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
- Additional Considerations
- Medication Interactions
Prednisone and Levofloxacin: A Detailed Overview
Consult your doctor before combining prednisone and levofloxacin. This combination may increase your risk of certain side effects.
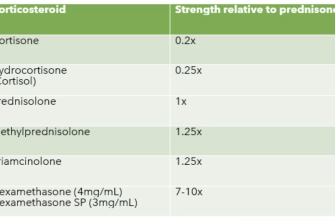
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system. Common side effects include weight gain, mood changes, and increased blood sugar. Long-term use carries additional risks like osteoporosis and cataracts.
Levofloxacin, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, fights bacterial infections. Potential side effects include tendon rupture, nausea, and dizziness. Rare, but serious, adverse reactions involve nerve damage and heart rhythm problems.
Taking both medications simultaneously might increase the likelihood of side effects from each drug. For instance, prednisone’s effect on blood sugar can be worsened by levofloxacin. Moreover, levofloxacin can exacerbate the risk of tendon problems already elevated by prednisone. The interaction primarily stems from the drugs’ effects on the body’s systems – corticosteroids impact the immune response, while fluoroquinolones interfere with cell function.
Specific monitoring is crucial. Your doctor should regularly check your blood sugar, liver function, and monitor for signs of tendon problems or other adverse reactions. They might adjust dosages or suggest alternative medications, depending on your individual health and the severity of your infection.
Always inform your physician about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting a new treatment plan. Open communication ensures appropriate medical management and minimizes potential complications.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek professional medical guidance for any health concerns or before making decisions related to your treatment.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Infection Treatment
Prednisone isn’t an antibiotic; it’s a corticosteroid. It doesn’t directly kill bacteria or viruses. Instead, it powerfully reduces inflammation. This is beneficial in some infectious diseases where inflammation itself contributes significantly to illness. For instance, severe bacterial pneumonia may involve overwhelming inflammation alongside infection. Prednisone can help manage this dangerous inflammation, easing breathing difficulties and improving overall condition.
Specific Situations Where Prednisone Might Be Used
Doctors might prescribe prednisone alongside antibiotics (like levofloxacin) for conditions such as severe bacterial pneumonia, certain types of meningitis, or other infections causing significant inflammation. It’s crucial to understand that prednisone doesn’t replace antibiotics; it supplements them. The antibiotics tackle the infection directly, while prednisone manages the inflammatory response.
However, prednisone use in infection treatment is carefully considered. It can suppress the immune system, potentially increasing the risk of developing other infections or worsening existing ones. Its use is usually reserved for serious cases where the benefits clearly outweigh the risks. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely and report any concerning symptoms immediately.
Levofloxacin: Mechanism of Action and Uses
Levofloxacin targets bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. These enzymes are crucial for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, and repair. By inhibiting these enzymes, levofloxacin prevents bacterial cell growth and ultimately leads to bacterial death.
This mechanism makes levofloxacin effective against a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Its specific spectrum of activity varies, depending on the bacterial strain’s susceptibility. Always consult local antibiograms for guidance.
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Levofloxacin treats bacterial pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis. It’s particularly useful for infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis.
- Skin and Skin Structure Infections: It’s commonly used to treat cellulitis, abscesses, and other skin infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Levofloxacin treats complicated and uncomplicated UTIs, including pyelonephritis. Consider culture and sensitivity testing before prescribing.
- Other Infections: Levofloxacin may be used for certain other infections, such as those affecting the bones and joints, and intra-abdominal infections. This should be done only under the guidance of a physician.
Remember, appropriate antibiotic stewardship is paramount. Always consider the local resistance patterns and individual patient factors before prescribing levofloxacin. Monitor patients closely for adverse effects, such as tendonitis or tendinopathy.
- Obtain a proper diagnosis before initiating treatment.
- Consider culture and sensitivity testing to guide treatment.
- Adhere to prescribed dosage and duration.
- Educate patients on potential side effects.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Potential Drug Interactions Between Prednisone and Levofloxacin
While generally considered safe when used together, Prednisone and Levofloxacin can interact, potentially increasing the risk of certain side effects. Close monitoring is crucial.
Here’s what you should know:
- Increased risk of tendon rupture: Prednisone weakens tendons, and Levofloxacin also carries this risk as a side effect. Combined use significantly elevates the chance of tendon injury, especially in older adults or those with existing tendon problems. Avoid strenuous activity.
- Elevated blood sugar levels: Prednisone can raise blood glucose. Individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar closely while taking both medications. Regular blood glucose testing is recommended.
- Increased risk of gastrointestinal problems: Both drugs can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. This risk increases when used together. Consider taking these medications with food to mitigate this.
- Central Nervous System Effects: Levofloxacin can cause dizziness and confusion. Prednisone, at higher doses, may exacerbate these effects. Exercise caution when operating machinery or driving.
Recommendations:
- Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Regularly monitor your blood glucose levels, especially if you have diabetes.
- Report any unusual symptoms, such as tendon pain, muscle weakness, or severe gastrointestinal distress, to your physician immediately.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of treatment for both medications.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist before starting, stopping, or changing any medication.
Common Side Effects When Taking Both Medications
Prednisone and levofloxacin, when taken together, can increase the likelihood of certain side effects. You might experience increased stomach upset, including nausea, vomiting, or heartburn. This is because prednisone can irritate the stomach lining, and levofloxacin can also cause gastrointestinal distress.
Headache is another common side effect. Prednisone can elevate blood pressure, potentially contributing to headaches, and levofloxacin can also induce headaches in some individuals. Staying hydrated may help mitigate this.
Both medications can affect your sleep. Prednisone can cause insomnia, while levofloxacin may lead to drowsiness or sleep disturbances. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule can be beneficial.
Changes in blood sugar levels are possible with prednisone, especially in individuals with diabetes. Close monitoring of blood sugar is recommended. Levofloxacin does not directly impact blood sugar but may indirectly influence it through its effects on other bodily functions.
Increased risk of infection is a concern. Prednisone suppresses the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. While levofloxacin is an antibiotic, it doesn’t fully compensate for the immunosuppressive effects of prednisone.
Monitor for signs of allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, or swelling. If any such reactions occur, discontinue use immediately and seek medical attention.
This information is not exhaustive; always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice and to report any concerns.
Specific Patient Considerations and Precautions
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This helps prevent dangerous drug interactions.
Diabetes Management
Prednisone can increase blood sugar levels. If you have diabetes, monitor your blood glucose closely and adjust your insulin or oral medication as needed, consulting your doctor for guidance. Frequent blood glucose checks are recommended.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Both prednisone and levofloxacin can cause stomach upset. Taking these medications with food can help minimize this side effect. Report any persistent nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain to your doctor immediately.
Mental Health Monitoring
Prednisone can sometimes affect mood, potentially causing anxiety or insomnia. Levofloxacin, in rare cases, has been linked to psychosis. Report any unusual changes in your mood or mental state to your doctor.
Infections
Levofloxacin is an antibiotic, but prednisone weakens the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or increased pain.
Liver and Kidney Function
Your doctor should monitor your liver and kidney function, particularly if you have pre-existing conditions affecting these organs. Regular blood tests may be necessary.
Allergies
Before starting these medications, inform your doctor of any known allergies to corticosteroids, quinolones, or other medications. Allergic reactions can be serious.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Discuss the use of prednisone and levofloxacin with your doctor if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant. These medications may not be appropriate for all situations.
Elderly Patients
Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of both prednisone and levofloxacin. Your doctor will adjust dosage and monitor you closely.
Children
Dosage adjustments are usually necessary for children. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on your child’s age and weight.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prednisone and Levofloxacin
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any severe allergic reactions, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, or hives. These are life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Seek medical advice if you develop unusual bruising or bleeding, experience persistent nausea or vomiting, notice significant changes in your mood or behavior (including anxiety or depression), or develop muscle weakness or pain. These could indicate serious side effects.
Also, call your doctor if your symptoms don’t improve or worsen after a few days of treatment. This is important for determining the effectiveness of the medication and adjusting the treatment plan accordingly.
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
If you have diabetes, closely monitor your blood sugar levels. Prednisone can significantly affect blood sugar control. Report any unusual changes to your doctor.
Additional Considerations
Regularly scheduled check-ups with your doctor are crucial while taking Prednisone and Levofloxacin. This allows for monitoring of potential side effects and adjustment of your medication as needed. Open communication is key to successful treatment.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Severe allergic reaction | Go to the emergency room immediately. |
| Unusual bruising or bleeding | Contact your doctor immediately. |
| Persistent nausea or vomiting | Contact your doctor immediately. |
| Significant mood changes | Contact your doctor immediately. |
| Muscle weakness or pain | Contact your doctor immediately. |
| No improvement in symptoms | Contact your doctor. |
| Worsening of symptoms | Contact your doctor. |
Medication Interactions
Inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential harmful interactions. This ensures the safest and most effective treatment.