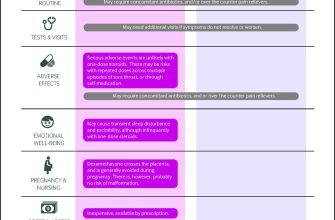
Prednisone can significantly reduce poison ivy inflammation. However, dosage depends heavily on the severity of your reaction. For mild rashes covering less than 10% of your body, a short course of 20-40mg daily for 5-7 days often suffices. Remember to follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
More extensive rashes, affecting a larger body surface area or involving the face or genitals, may require higher dosages and longer treatment durations. Your physician might prescribe 40-60mg daily for 7-14 days, potentially tapering down the dose gradually thereafter to minimize side effects. Always discuss any concerns about side effects with your doctor.
Children require adjusted dosages based on weight and age. Never administer prednisone to a child without a doctor’s explicit prescription and guidance. They’ll determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on your child’s specific needs.
Severe reactions necessitate immediate medical attention. Intense swelling, difficulty breathing, or widespread blistering demand a prompt visit to the emergency room or urgent care clinic. Prednisone may be part of a broader treatment plan in such cases, but it’s not a standalone solution for severe reactions.
This information provides general guidelines only. Individual needs vary greatly. Consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider to determine the right prednisone dosage for your particular situation. They can accurately assess your condition and provide personalized advice.
- Poison Ivy and Prednisone Dosage
- Identifying Poison Ivy Reactions Requiring Prednisone
- Severe Symptoms Warranting Prednisone
- When to Consider Prednisone for Less Extensive Reactions
- Consulting a Doctor
- Determining the Severity of Your Poison Ivy Rash
- Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage for Poison Ivy
- Individual Patient Factors
- Treatment Goals and Duration
- Monitoring and Adjustments
- Alternative Treatments
- Standard Prednisone Dosage Regimens for Poison Ivy
- Factors Influencing Dosage
- Alternative Regimens
- Tapering Off Prednisone: A Crucial Step
- Understanding Your Tapering Schedule
- Monitoring Your Body’s Response
- Potential Side Effects During Tapering
- Example Tapering Schedule
- Post-Tapering Monitoring
- Potential Side Effects of Prednisone for Poison Ivy
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Poison Ivy and Prednisone
Poison Ivy and Prednisone Dosage
Prednisone isn’t a first-line treatment for poison ivy; however, your doctor might prescribe it for severe cases. Dosage depends entirely on the severity of your reaction and your individual health. Typical oral prednisone courses range from 5 to 10 days.
A common starting dose is 40-60mg daily, tapered down over several days. For example, a doctor might prescribe 60mg on day one, then 40mg on day two, 20mg on day three and so on. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions; don’t adjust your dosage without consulting them. The goal is to manage symptoms while minimizing side effects.
Severe reactions, including widespread blistering or significant swelling, may necessitate higher initial doses and longer treatment courses. Conversely, mild cases might require lower doses or even topical corticosteroids instead of oral prednisone.
Possible side effects include increased appetite, weight gain, insomnia, mood changes, and increased blood sugar. Discuss these potential effects with your physician before starting treatment. Regular monitoring, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions, is important.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of poison ivy and before starting any medication.
Identifying Poison Ivy Reactions Requiring Prednisone
Seek medical attention if your poison ivy reaction covers more than 20% of your body surface area. This signifies a significant reaction needing stronger intervention.
Severe Symptoms Warranting Prednisone
Severe blistering and swelling, especially involving the face or genitals, requires immediate medical evaluation and likely prednisone. Look for widespread blistering, significant swelling that restricts movement, and oozing lesions.
High fever accompanying the rash indicates a systemic infection possibly requiring prednisone and other antibiotics. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience a fever above 101°F (38.3°C).
When to Consider Prednisone for Less Extensive Reactions
Intense itching causing significant sleep disruption or impacting your daily activities might justify prednisone, especially if topical treatments prove insufficient. Consider prednisone if over-the-counter remedies fail to provide relief after a reasonable trial period (typically a few days).
Significant pain associated with the rash should be addressed with your doctor; Prednisone can help manage this discomfort, particularly when severe.
Consulting a Doctor
Don’t hesitate to contact a doctor if you have any doubts about the severity of your reaction. They can assess your specific case and determine the most appropriate treatment plan, which may or may not include prednisone.
Determining the Severity of Your Poison Ivy Rash
Assess your rash based on these factors:
- Extent of the rash: How much of your body is affected? A small, localized rash is less severe than a widespread rash covering a large area.
- Number of blisters: Count the number of blisters present. More blisters generally indicate a more significant reaction.
- Blister size and appearance: Note the size and appearance of the blisters. Large, fluid-filled blisters might indicate a more severe reaction than small, dry lesions.
- Swelling: Is there significant swelling beyond the rash itself? Increased swelling, particularly in the face or throat, demands immediate medical attention.
- Symptoms beyond the rash: Are you experiencing fever, chills, or swollen lymph nodes? These indicate a more serious systemic reaction.
- Pain and itching: Rate the intensity of pain and itching on a scale of 1-10. Intense discomfort might warrant medical intervention.
Here’s a simple severity guide:
- Mild: Small, localized rash with minimal itching and few, small blisters.
- Moderate: Larger rash area, more numerous blisters, noticeable itching and some discomfort.
- Severe: Widespread rash, numerous large blisters, significant swelling, intense itching and pain, and potentially systemic symptoms (fever, chills, etc.). Seek medical attention immediately.
Use this assessment to guide your decision about seeking medical help. Remember that even mild cases can worsen without treatment. Always consult a doctor if you have concerns.
Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage for Poison Ivy
Your doctor determines your prednisone dosage based on several key factors. Severity of your rash is paramount; widespread, blistering reactions require higher doses than mild cases. The extent of your reaction, measured by the affected skin surface area, directly impacts the prescribed amount.
Individual Patient Factors
Your age and overall health significantly influence dosage. Children generally receive lower doses adjusted for their weight. Pre-existing conditions, particularly those affecting your immune system or liver, necessitate careful dose adjustments to minimize potential side effects. Your body’s response to previous medication, including any allergies, also informs dosage decisions. A patient’s weight plays a significant role; higher weight might justify a slightly higher dose, calculated per kilogram.
Treatment Goals and Duration
The objective of prednisone treatment–rapid symptom control or long-term management–also dictates dosage. High initial doses might be used for severe cases aiming for rapid symptom relief, followed by a gradual tapering of the medication. The treatment duration directly correlates with the severity; minor reactions might require only a short course, while severe cases demand longer treatment schedules. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding the dosage and length of treatment.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular monitoring of your symptoms and potential side effects is crucial. Your doctor will adjust the prednisone dosage based on your response and tolerance. Blood tests might be necessary to monitor liver function. Close collaboration with your healthcare provider ensures optimal treatment and minimizes adverse effects. Remember, never adjust your prednisone dosage without consulting your doctor.
Alternative Treatments
Prednisone isn’t always the first-line treatment for poison ivy. Your doctor may consider other options like topical corticosteroids or antihistamines depending on the severity and your individual circumstances. Always discuss all treatment options with your physician to determine the best course of action for you.
Standard Prednisone Dosage Regimens for Poison Ivy
Doctors typically prescribe a short course of prednisone for severe poison ivy reactions. A common regimen involves a high initial dose, gradually tapering down over several days. For example, a patient might start with 40mg daily for a few days, then reduce to 30mg, then 20mg, 10mg, and finally 5mg before stopping completely. The exact duration and tapering schedule depend on the severity of the rash and the patient’s response. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Your doctor will consider several factors when determining the appropriate prednisone dose. These include the extent of your rash, your overall health, and any other medications you’re taking. Children and older adults may require adjusted dosages. A more extensive rash might warrant a higher initial dose or a longer treatment course. Be sure to discuss any concerns you have with your physician.
Alternative Regimens
While the tapering regimen described above is common, your doctor might prescribe a different approach depending on your needs. Some patients may benefit from a shorter course with a quicker reduction in dosage. Others may require a longer course for persistent symptoms. It’s crucial to follow your doctor’s personalized plan.
Tapering Off Prednisone: A Crucial Step
Never stop prednisone abruptly. Your doctor will create a tapering schedule, gradually reducing your dose. This prevents adrenal insufficiency, a potentially serious condition where your body doesn’t produce enough cortisol.
Understanding Your Tapering Schedule
Your doctor will provide specific instructions. A common approach involves decreasing the dose by a small amount (e.g., 5mg) every few days or a week. The pace depends on factors including your initial dose and your body’s response. Closely follow your doctor’s plan.
Monitoring Your Body’s Response
Pay close attention to how your body reacts. Report any new or worsening symptoms, such as fatigue, muscle weakness, nausea, or dizziness, to your doctor immediately. These might indicate adrenal insufficiency requiring adjustments to your tapering schedule.
Potential Side Effects During Tapering
Expect some side effects as your body adjusts. These may include fatigue, headaches, and joint pain. These are usually manageable and temporary. Your doctor can help manage these with medication or suggest lifestyle modifications.
Example Tapering Schedule
| Day | Prednisone Dose (mg) |
|---|---|
| 1-7 | 40 |
| 8-14 | 35 |
| 15-21 | 30 |
| 22-28 | 25 |
| 29-35 | 20 |
| 36-42 | 15 |
| 43-49 | 10 |
| 50-56 | 5 |
| 57+ | 0 |
Disclaimer: This is a sample schedule. Your individual schedule will vary greatly depending on your specific needs and your doctor’s assessment. Do not use this table as a guide without consulting your doctor. They will tailor a plan specifically for you.
Post-Tapering Monitoring
Even after completing your taper, schedule follow-up appointments with your doctor. They will monitor your adrenal function and overall health. This ensures a smooth transition and addresses any lingering issues.
Potential Side Effects of Prednisone for Poison Ivy
Prednisone effectively reduces poison ivy inflammation, but it’s crucial to understand potential side effects. These vary by dosage and individual sensitivity. Common side effects include increased appetite and weight gain. You might also experience insomnia or mood swings.
More serious, though less frequent, side effects involve increased blood sugar levels, potentially triggering problems for diabetics. Increased blood pressure and thinning of bones (osteoporosis) are also possibilities, especially with prolonged use. Fluid retention leading to swelling (edema) can occur.
Gastrointestinal issues such as heartburn, nausea, and ulcers are also potential concerns. Prednisone can also weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Skin changes like bruising and thinning skin are also possible.
Remember to discuss all potential side effects with your doctor before starting prednisone treatment. They can assess your individual risk factors and help you manage any side effects that develop. Promptly report any unusual symptoms or worsening of existing conditions.
Your doctor will likely prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to control your poison ivy symptoms. This minimizes potential side effects. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Poison Ivy and Prednisone
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing or swallowing after contact with poison ivy, even if you’re already taking prednisone. This suggests a severe allergic reaction.
Contact your doctor if:
- Your rash covers a large area of your body (more than 20% of your skin).
- The rash is spreading rapidly or worsening despite prednisone.
- You develop a fever, chills, or swollen lymph nodes.
- Your symptoms don’t improve within a week of starting prednisone treatment.
- You experience severe itching that interferes with sleep or daily activities.
- You have secondary skin infections (signs include increased pus, yellow crusts, or streaking red lines).
- You develop blisters that are weeping, oozing, or are extremely painful.
Prednisone is a powerful medication with potential side effects. Discuss these concerns with your doctor before starting treatment. Report any unusual side effects, such as increased thirst, frequent urination, or significant mood changes immediately.
Children and individuals with pre-existing health conditions should consult a doctor before using prednisone for poison ivy treatment. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and monitor your progress to ensure safe and effective management.
- Accurate diagnosis is key. A doctor can confirm poison ivy and rule out other conditions.
- Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on your response.
- Proper monitoring reduces the risk of side effects.