Need to understand the differences between methylprednisolone and prednisone? Focus on their distinct metabolic pathways. Methylprednisolone boasts a longer half-life, meaning fewer daily doses. Prednisone, conversely, requires more frequent administration due to its faster metabolism.
Consider your specific needs. Methylprednisolone’s prolonged action makes it ideal for managing conditions requiring sustained anti-inflammatory effects, such as severe asthma exacerbations. Prednisone, with its quicker onset and shorter duration, might be better suited for treating acute inflammatory responses, like a flare-up of rheumatoid arthritis.
Dosage is crucial. Always follow your doctor’s instructions meticulously. They’ll tailor the regimen based on your individual health status and the severity of your condition. Incorrect dosage can lead to significant side effects.
Side effects vary depending on the drug and the individual. Common side effects include increased appetite, weight gain, and mood changes. Serious side effects, though less frequent, necessitate immediate medical attention. Discuss potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider.
Remember, this information provides a general overview. Self-treating can be harmful. Consult your physician for personalized guidance and treatment recommendations. They possess the expertise to evaluate your condition and make informed decisions regarding the best medication for you.
Methylprednisolone vs. Prednisone: A Detailed Comparison
Choose Methylprednisolone for faster, more potent anti-inflammatory action, particularly in acute situations requiring rapid response. Prednisone suits longer-term management of less severe conditions.
Potency: Methylprednisolone boasts five times the anti-inflammatory power of Prednisone. This difference impacts treatment duration and dosage. Expect lower doses of Methylprednisolone for comparable effects.
Absorption: Prednisone requires liver metabolism before becoming active. Methylprednisolone is active immediately after administration, offering quicker relief.
Administration: Both drugs come in oral, intravenous, and injectable forms. Intravenous Methylprednisolone offers the most rapid onset, ideal for severe flare-ups.
Side Effects: Both drugs share common side effects like weight gain, fluid retention, and increased blood sugar. However, higher potency of Methylprednisolone might increase the risk of these side effects with higher doses.
Specific Uses: Methylprednisolone frequently treats severe conditions like allergic reactions, asthma exacerbations, and inflammatory bowel disease flares. Prednisone often manages autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus over extended periods.
Dosage and Duration: Dosing varies drastically depending on the condition’s severity and the patient’s response. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Treatment duration also depends on the specific condition and the prescribed drug. Your healthcare provider will determine the optimal course.
Note: This information serves as a general comparison. Consult a physician before making any decisions regarding your medication.
Understanding the Differences in Their Use and Effects
Methylprednisolone and prednisone are both corticosteroids, but differ in their absorption and duration of action. Methylprednisolone is absorbed faster, leading to a quicker onset of effects. Prednisone, conversely, needs to be converted by the liver into its active form, resulting in a slower but potentially longer-lasting impact.
This difference in absorption influences their application. Doctors frequently prefer methylprednisolone for acute conditions requiring rapid relief, such as severe allergic reactions or flare-ups of inflammatory diseases. Its rapid action allows for quicker symptom control. Prednisone, however, often proves more suitable for long-term management of chronic conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis due to its extended duration of action.
Dosage also varies significantly. Methylprednisolone doses are often higher initially for rapid effect but may be tapered down quickly. Prednisone dosages tend to be lower but are administered for longer periods. The prescribed regimen specifically depends on the individual’s condition, response to treatment and other health factors. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Side effects, while potentially similar, can manifest differently. Since methylprednisolone acts faster, some side effects might appear more rapidly. Long-term use of either medication can lead to issues like weight gain, high blood pressure, and increased risk of infection. Careful monitoring by a physician is crucial for managing these potential side effects.
In short: Methylprednisolone provides faster relief for acute conditions, while prednisone is better suited for long-term management of chronic illnesses. Your doctor will consider your specific needs and health status to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage.
Side Effects and Potential Risks: A Practical Guide
Monitor yourself closely for any unusual symptoms. Report them immediately to your doctor.
Methylprednisolone and prednisone, while highly effective, can cause various side effects. The severity varies depending on dosage and duration of use.
- Increased blood sugar: This is common, particularly in individuals with diabetes. Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial. Your doctor might adjust your diabetes medication.
- Weight gain: Fluid retention and increased appetite contribute to weight gain. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help mitigate this.
- Mood changes: Some experience irritability, anxiety, or even depression. Open communication with your doctor and support system is vital.
- Increased risk of infection: These medications suppress the immune system. Practice good hygiene and avoid contact with sick individuals.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Heartburn, nausea, and ulcers are possible. Your doctor might prescribe medication to protect your stomach lining.
- Muscle weakness: This can be significant with prolonged use. Gentle exercise and a calcium-rich diet can help.
- Osteoporosis: Long-term use increases the risk of bone thinning. Discuss bone density testing and preventative measures with your doctor.
- Cataracts and glaucoma: Eye exams are recommended during treatment, especially with long-term use.
- High blood pressure: Regular blood pressure checks are necessary. Your doctor might prescribe medication to manage blood pressure.
These are not all possible side effects. This list provides a practical overview of common concerns. Always consult your physician or pharmacist for complete information specific to your health situation. They can help manage potential side effects and ensure the safest possible treatment.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Don’t adjust your dosage without consulting them.
- Report any concerning symptoms promptly. Early intervention can often mitigate potential problems.
- Maintain open communication with your healthcare team. They are your best resource for managing potential risks.
Making Informed Decisions with Your Doctor: Questions to Ask
Before starting methylprednisolone or prednisone, ask your doctor about specific potential side effects relevant to your health conditions and medications. For example, inquire about the risk of increased blood sugar if you have diabetes, or osteoporosis if you have a family history of bone fragility.
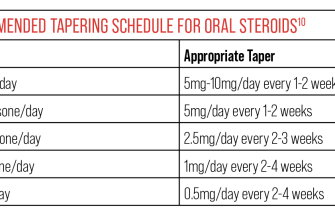
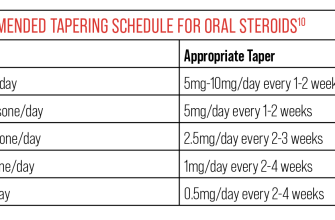
Discuss the treatment duration. Ask how long you’ll likely be on the medication and what the tapering schedule will be. Understand the rationale behind the prescribed dosage and frequency.
Inquire about alternative treatments. Are there other options besides methylprednisolone or prednisone that might be suitable for your condition? Discuss the pros and cons of each approach.
Ask about potential drug interactions. Provide your doctor with a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are currently taking. This helps prevent unforeseen complications.
Clarify monitoring plans. What tests or check-ups will you need during treatment? How will your doctor track your progress and adjust the medication as necessary?
Get clear instructions on what to do if you experience side effects. Know what symptoms require immediate medical attention and what can be managed at home.
Ask about the medication’s effects on your daily life. Will it affect your ability to drive, work, or participate in your normal activities? Discuss strategies to mitigate any potential impact.
Finally, don’t hesitate to ask your doctor to explain anything you don’t understand. Clear communication is key to successful treatment.