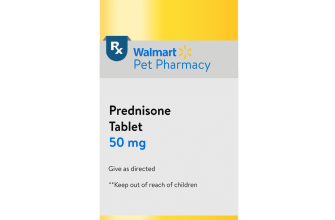
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Prednisone dosage varies greatly depending on your specific condition, age, and overall health. Typical starting doses range from 5mg to 60mg daily, but this is just a broad guideline. Your physician will determine the appropriate starting dose and adjustment schedule based on your individual needs.
Taking Prednisone with food can minimize stomach upset, a common side effect. Remember to swallow the pills whole; crushing or chewing can alter absorption and effectiveness. A consistent daily schedule is crucial. Taking your medication at the same time each day helps maintain consistent blood levels.
Never suddenly stop taking Prednisone. Stopping abruptly can cause serious withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will carefully guide you through a gradual tapering-off process to minimize these risks. This process typically involves slowly reducing your daily dosage over several weeks or even months, depending on the duration of your treatment and your body’s response.
Monitor for potential side effects. Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, fluid retention, mood changes, and increased blood sugar. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately. They can help manage side effects and adjust your treatment plan as needed. Regular check-ups are important to track your progress and address any complications.
- Prednisone Usage and Dosage: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone: Its Uses and Mechanisms
- Autoimmune Disorders and Inflammatory Conditions
- Allergic Reactions and Other Uses
- Mechanism of Action
- Important Note:
- Starting Prednisone: Initial Dosage and Administration
- Taking Prednisone: Practical Tips
- Potential Side Effects and Management
- Adjusting Prednisone Dosage: Tapering and Maintenance
- Tapering Schedules
- Monitoring Your Body
- Maintenance Dosage
- Important Considerations
- Potential Long-Term Effects and Alternate Treatments
- Potential Side Effects of Prednisone and Management Strategies
- Prednisone and Interactions: Medications and Lifestyle Factors
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Vaccinations and Infections
- Monitoring Prednisone Therapy: Important Considerations and Follow-up
- Blood Pressure and Weight Monitoring
- Blood Sugar and Glucose Monitoring
- Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
- Laboratory Tests
- Medication Adjustments and Tapering
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Open Communication
- Follow-up Appointments
Prednisone Usage and Dosage: A Detailed Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Prednisone dosage varies greatly depending on the condition being treated and the individual’s response. Typical starting doses range from 5mg to 60mg daily, often in divided doses.
Your doctor will likely adjust your dosage over time. They might start with a higher dose to achieve rapid symptom control, then gradually taper the dose down to the lowest effective amount to minimize side effects. Sudden cessation can cause withdrawal symptoms, so gradual reduction is vital.
Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, fluid retention, mood changes, and increased blood sugar. Inform your doctor immediately about any concerning side effects.
Prednisone can interact with other medications. Be sure to disclose all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking to your doctor or pharmacist. Some medications shouldn’t be taken concurrently with Prednisone.
| Dosage Form | Typical Doses | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Oral Tablets | 5mg, 10mg, 20mg | Swallow whole with water. |
| Oral Solution | Variable concentrations | Follow instructions on the label carefully. |
Long-term use of Prednisone increases the risk of certain health problems, including osteoporosis, cataracts, and infections. Your doctor may recommend preventative measures like calcium supplements or regular eye exams.
This guide offers general information; it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on Prednisone usage and dosage. They can tailor a treatment plan to your specific needs and monitor your progress.
Understanding Prednisone: Its Uses and Mechanisms
Prednisone, a glucocorticoid, powerfully reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system. Doctors prescribe it for various conditions requiring rapid symptom relief.
Autoimmune Disorders and Inflammatory Conditions
Prednisone effectively manages autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis by dampening the body’s overactive immune response. It also treats inflammatory conditions such as asthma and inflammatory bowel disease, significantly reducing swelling and irritation.
Allergic Reactions and Other Uses
Beyond autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, prednisone provides relief from severe allergic reactions and certain cancers. It’s also used for conditions like multiple sclerosis and certain eye problems. Dosage varies widely depending on the specific condition and its severity. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Mechanism of Action
Prednisone acts by binding to glucocorticoid receptors within cells. This binding triggers a cascade of events, ultimately decreasing the production of inflammatory chemicals, thus reducing swelling, redness, and pain. It also impacts the immune system by reducing the activity of immune cells involved in inflammation. Remember, Prednisone is a potent medication; understanding its uses and how it works is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
Important Note:
Never adjust your prednisone dosage without consulting your physician. Sudden cessation can lead to serious withdrawal symptoms. Always discuss potential side effects and long-term implications with your healthcare provider.
Starting Prednisone: Initial Dosage and Administration
Your doctor will determine your starting Prednisone dosage based on your specific condition and health. Typical initial doses range from 5 to 60 milligrams daily, often administered as a single dose in the morning. Higher doses are usually reserved for severe conditions requiring rapid symptom control.
Taking Prednisone: Practical Tips
Prednisone is typically taken orally with a glass of water. Avoid taking it with food that contains calcium or magnesium, as these minerals can interfere with absorption. Follow your physician’s instructions carefully; never adjust the dosage or stop taking Prednisone without consulting them. Consistent timing is key for optimal results. Many find taking the medication at the same time each morning improves consistency. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up doses.
Potential Side Effects and Management
Prednisone’s side effects vary depending on the dosage and duration of treatment. Common side effects include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. Your doctor will monitor you for these and other potential complications, and provide strategies for managing them. Open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial during Prednisone therapy.
Adjusting Prednisone Dosage: Tapering and Maintenance
Never abruptly stop Prednisone. Always reduce your dosage gradually, a process called tapering. This prevents adrenal insufficiency, where your body can’t produce enough cortisol.
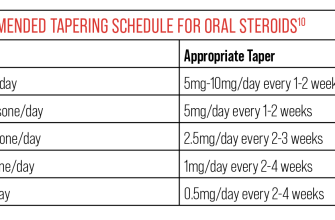
Tapering Schedules
Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule, but here are common examples:
- Slow Taper (for higher doses or long-term use): Decrease the dose by 2.5-5mg every 3-7 days.
- Moderate Taper: Decrease the dose by 5-10mg every few days, depending on your response.
- Fast Taper (rarely used): More rapid reductions, usually under strict medical supervision, for short-term use and mild symptoms.
Tapering speed depends on factors such as your initial dose, treatment duration, and your body’s response.
Monitoring Your Body
During tapering, carefully monitor for signs of adrenal insufficiency, including fatigue, weakness, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Report any concerning symptoms to your physician immediately.
Maintenance Dosage
Sometimes, a maintenance dose is necessary for ongoing management of certain conditions. This dose is much lower than the initial treatment dose and is designed to keep symptoms controlled. Your doctor will carefully determine the appropriate maintenance dose and adjust it as needed based on your health status and response to treatment. Regular blood tests may be required.
Important Considerations
- Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
- Do not adjust your dose without consulting your doctor.
- Keep all scheduled appointments for monitoring.
- Learn about the potential side effects of Prednisone and report any new or worsening symptoms.
Potential Long-Term Effects and Alternate Treatments
Long-term Prednisone use carries risks such as osteoporosis, weight gain, and increased risk of infections. Your doctor may discuss alternative treatments or strategies to minimize long-term side effects. Discuss your concerns and treatment goals with your doctor to create a plan that’s right for you.
Potential Side Effects of Prednisone and Management Strategies
Prednisone, while highly effective, carries potential side effects. These vary depending on dosage and duration of treatment. Common side effects include weight gain, particularly in the face and abdomen (moon face, buffalo hump), increased appetite, fluid retention, high blood pressure, insomnia, and mood changes (irritability, anxiety, depression).
Higher doses and longer treatment periods increase the risk of more serious side effects such as osteoporosis, increased risk of infections, cataracts, glaucoma, and stomach ulcers. Some individuals experience muscle weakness and thinning of the skin.
Managing these side effects involves close monitoring by your doctor. Regular blood pressure checks are vital. Dietary modifications, including reducing sodium intake and increasing calcium and vitamin D intake, help mitigate weight gain and bone density loss. Regular exercise can counteract muscle weakness and improve overall health.
For insomnia, your doctor may suggest adjusting the timing of your dose, or prescribe a sleep aid. If mood changes are significant, counseling or antidepressants may be helpful. Regular eye exams are recommended to monitor for cataracts and glaucoma. Your doctor may prescribe medication to protect your stomach lining if ulcers are a concern.
Open communication with your doctor is paramount. Report any concerning symptoms immediately. They can adjust your dosage, prescribe additional medications, or recommend lifestyle changes to minimize side effects and maximize the benefits of Prednisone therapy.
Prednisone and Interactions: Medications and Lifestyle Factors
Always inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins. Prednisone can interact negatively with many drugs, potentially increasing the risk of side effects or reducing their effectiveness. For instance, concurrent use with blood thinners like warfarin requires careful monitoring to prevent excessive bleeding. Similarly, combining prednisone with NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like ibuprofen or naproxen raises the chance of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Diabetes medications may need adjustment, as prednisone can increase blood sugar levels. It’s also crucial to discuss any heart medications, immunosuppressants, or antibiotics you’re using.
Lifestyle Modifications
Prednisone use necessitates lifestyle adjustments. Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein to mitigate potential weight gain and metabolic disturbances. Regular exercise helps manage weight and stress, both important factors when taking prednisone. Limit alcohol consumption as it can exacerbate liver problems and interact negatively with prednisone. Finally, prioritize sufficient sleep to support overall health and reduce stress levels, contributing to better management of potential side effects.
Vaccinations and Infections
Prednisone weakens the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections. Avoid contact with sick individuals, practice good hygiene, and discuss vaccination strategies with your doctor. Certain live vaccines should be avoided during prednisone treatment. Report any signs of infection–fever, cough, or unusual fatigue–promptly to your physician.
Monitoring Prednisone Therapy: Important Considerations and Follow-up
Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor. Frequency depends on your dosage and overall health, but expect at least monthly visits, especially during initial treatment and higher doses.
Blood Pressure and Weight Monitoring
Monitor your blood pressure regularly at home and report any significant changes to your doctor. Prednisone can elevate blood pressure. Weigh yourself weekly to track fluid retention, another potential side effect.
Blood Sugar and Glucose Monitoring
If you have diabetes, or are at risk, closely monitor your blood sugar levels. Prednisone can increase blood glucose. Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
- Increased thirst and urination
- Blurred vision
- Muscle weakness
- Mood changes (irritability, anxiety, depression)
- Increased risk of infections
- Osteoporosis risk (bone thinning)
- Significant weight gain or loss
- Easy bruising or bleeding
Report any of these symptoms immediately to your physician. Early detection allows for timely intervention and management.
Laboratory Tests
Your doctor will likely order regular blood tests to monitor your:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Electrolytes
- Liver function tests
- Kidney function tests
These tests help assess your overall health and detect any potential side effects.
Medication Adjustments and Tapering
Never abruptly stop taking prednisone. Your doctor will create a tapering schedule to gradually reduce your dosage, minimizing withdrawal symptoms. Strictly adhere to this schedule.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintain a healthy diet, focusing on fruits, vegetables, and lean protein.
- Engage in regular low-impact exercise as tolerated.
- Get adequate rest and manage stress levels.
- Follow your doctor’s guidance on calcium and vitamin D supplementation to mitigate osteoporosis risk.
Open Communication
Maintain open communication with your healthcare provider. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns or questions about your treatment. Proactive monitoring and communication are key to successful prednisone therapy.
Follow-up Appointments
Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments. Your doctor will assess your progress, adjust your medication as needed, and provide guidance on managing potential side effects.