Taking 20mg of prednisone daily requires careful monitoring. This dosage is often used for moderate to severe inflammation, but its long-term use carries potential side effects. Consult your doctor regularly to adjust the dosage as needed and minimize risks.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. They will tailor the treatment plan based on your specific health condition and response to the medication. Never alter your dosage without first consulting them. Regular blood tests can help monitor your body’s response to prednisone and identify potential issues early.
Potential side effects at this dosage can include weight gain, increased blood sugar, mood changes, and bone thinning. Open communication with your physician is key to managing these potential effects. They may suggest strategies for mitigating these issues, such as dietary changes or additional medications.
Remember, prednisone is a powerful medication. Understanding its effects and potential risks, along with proactive monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider, will ensure the safest and most effective treatment.
- 20 mg Prednisone a Day: A Detailed Overview
- Managing Side Effects
- Long-Term Use Considerations
- Dosage Tapering
- Understanding Prednisone and its Uses
- Common Side Effects of 20mg Prednisone Daily
- Metabolic Changes
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Potential Long-Term Effects of High-Dose Prednisone
- Metabolic Changes
- Other Potential Long-Term Effects
- Managing Long-Term Effects
- Disclaimer:
- Managing Side Effects: Practical Tips and Strategies
- Managing Weight Gain
- Managing Mood Changes
- Important Considerations for Children and the Elderly
- Children’s Specific Needs
- Elderly Patients: Unique Challenges
- General Recommendations for Both Groups
- Drug Interactions: What to Avoid While on Prednisone
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants)
- Potassium-Depleting Diuretics
- Diabetes Medications
- Vaccines
- Other Medications
- Herbal Supplements and Over-the-Counter Medications
- Alcohol
- Remember:
- Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe and Gradual Approach
- Monitoring for Side Effects
- Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
- Alternative Treatments
- Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
- Staying in Touch
- When to Consult Your Doctor: Recognizing Warning Signs
- Changes in Your Prednisone Dosage
- Other Concerns
20 mg Prednisone a Day: A Detailed Overview
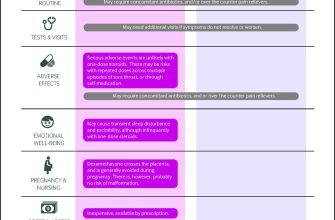
Twenty milligrams of prednisone daily is a moderate dose, often prescribed for inflammatory conditions. This dosage requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects. Regular blood tests are usually recommended to track your blood pressure, blood sugar, and potassium levels. Your doctor will adjust the dosage based on your response and these results.
Managing Side Effects
Common side effects at this dose include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, insomnia, and increased risk of infection. To mitigate weight gain, focus on a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Regular exercise, even short walks, helps manage weight and improve mood. Addressing insomnia might involve maintaining a regular sleep schedule and avoiding caffeine before bed. If you experience significant mood changes, discuss them openly with your doctor; they may suggest strategies or adjustments to your treatment.
Long-Term Use Considerations
Long-term use of prednisone, even at this dose, carries risks of osteoporosis, cataracts, and increased blood sugar. Your physician should discuss preventative measures, such as calcium and vitamin D supplements for bone health, and regular eye exams. If you have diabetes or risk factors, careful blood sugar monitoring is crucial.
Dosage Tapering
Never stop taking prednisone suddenly. Abrupt cessation can trigger adrenal insufficiency, a serious condition. Your doctor will develop a gradual tapering schedule to allow your body to adjust naturally. This schedule is personalized to your individual needs and treatment response. Closely follow your physician’s instructions during the tapering process.
Understanding Prednisone and its Uses
Prednisone is a corticosteroid medication, a powerful anti-inflammatory drug. Doctors prescribe it to reduce swelling, inflammation, and allergic reactions.
Common uses include: treating autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis; managing severe allergies; reducing inflammation in conditions such as asthma and bronchitis; and addressing symptoms of certain cancers.
Specific dosages vary greatly depending on your condition and response to treatment. Your doctor determines the correct dose and duration based on your individual needs. They will carefully monitor your progress and adjust the dose accordingly.
Prednisone works by suppressing the immune system. This means it can help reduce the body’s overreaction to various stimuli. However, this also means increased susceptibility to infections.
Potential side effects can include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, high blood pressure, and increased blood sugar. Regular checkups help your doctor manage these risks.
Remember to inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking to avoid potential drug interactions. Never stop taking prednisone abruptly; your doctor will guide you through a safe tapering schedule to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Prednisone is a powerful medicine, and proper use is crucial for safety and effectiveness.
Common Side Effects of 20mg Prednisone Daily
Taking 20mg of prednisone daily can cause several side effects. These vary from person to person, but awareness is key to managing them. Let’s look at some common ones.
Metabolic Changes
Weight gain is frequent, often due to increased appetite and fluid retention. Monitor your weight and diet accordingly. Increased blood sugar levels are also possible, requiring blood glucose monitoring, especially if you have diabetes or a family history of it. Prednisone can also raise cholesterol levels; regular checkups with your doctor are vital to monitor these changes.
Other Potential Side Effects
You might experience increased blood pressure. Regular monitoring is advisable. Mood swings, including irritability and anxiety, are also relatively common. Insomnia can be a problem. To minimize these, maintain a regular sleep schedule and avoid caffeine before bed.
| Side Effect | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
| Weight gain | Balanced diet, regular exercise |
| Increased blood sugar | Regular blood glucose monitoring, dietary adjustments |
| High blood pressure | Regular blood pressure checks, lifestyle changes |
| Mood swings | Stress management techniques, support system |
| Insomnia | Regular sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine before bed |
Gastrointestinal Issues
Some people experience heartburn or indigestion. Eating smaller, more frequent meals might help. In more severe cases, consult your doctor.
Remember, this information is not a substitute for medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have concerns about prednisone side effects or experience anything unusual.
Potential Long-Term Effects of High-Dose Prednisone
Taking 20mg of prednisone daily is considered a high dose, and prolonged use can lead to several significant side effects. Understanding these potential consequences is key to informed decision-making alongside your doctor.
Metabolic Changes
- Weight gain: Prednisone can cause fluid retention and increased appetite, leading to significant weight gain. Regular exercise and a balanced diet are crucial for mitigating this.
- Increased blood sugar: Prednisone can elevate blood glucose levels, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Regular blood sugar monitoring is necessary, especially for those with pre-existing conditions.
- High blood pressure: Prednisone can raise blood pressure. Regular monitoring and potential adjustments to medication are critical.
- Increased cholesterol: Prednisone may lead to an increase in cholesterol levels, raising the risk of cardiovascular disease. Dietary changes and medication may be necessary.
Other Potential Long-Term Effects
- Osteoporosis: Long-term prednisone use weakens bones, increasing the risk of fractures. Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation, alongside weight-bearing exercise, are recommended.
- Muscle weakness (myopathy): Prednisone can cause muscle wasting and weakness. Regular physical therapy may help maintain strength.
- Skin thinning: Prednisone can thin the skin, making it more susceptible to bruising and injury. Using gentle skincare products and avoiding harsh chemicals are beneficial.
- Cataracts and glaucoma: Prednisone can increase the risk of developing cataracts and glaucoma, requiring regular eye exams.
- Immunosuppression: Prednisone weakens the immune system, increasing vulnerability to infections. Practicing good hygiene and seeking prompt medical attention for any signs of infection is vital.
- Mood changes: Prednisone can cause mood swings, anxiety, and depression. Open communication with your doctor and potentially therapy are important.
Managing Long-Term Effects
Regular monitoring by your physician is paramount to minimize risks. This includes routine blood tests to check blood sugar, cholesterol, and other vital indicators. A collaborative approach, involving dietary adjustments, exercise, and potential supplementary medications, is crucial for managing long-term effects and improving overall health.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult your doctor before making any decisions related to your medication.
Managing Side Effects: Practical Tips and Strategies
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help your body process the medication and stay hydrated. This is especially important given prednisone’s potential to increase fluid retention.
Eat a balanced diet rich in potassium. Prednisone can deplete potassium, so focus on potassium-rich foods like bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach. Consult your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
Maintain regular exercise. Gentle activities like walking can help manage weight gain and improve overall well-being, although you should avoid strenuous exercise, especially during initial stages of treatment.
Managing Weight Gain
Monitor your weight regularly. Sudden weight changes are a potential side effect. If you notice significant weight gain, discuss it with your doctor. They can help adjust your treatment plan or suggest strategies for weight management.
Choose lean protein sources and limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. Small, frequent meals can help manage appetite.
Managing Mood Changes
Prioritize sleep hygiene. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night to help stabilize mood. Create a relaxing bedtime routine.
Engage in stress-reducing activities, like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. Talk to a trusted friend, family member, or therapist if you are experiencing significant mood swings or anxiety.
| Side Effect | Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| Increased appetite | Smaller, more frequent meals; healthy snack choices |
| Insomnia | Relaxing bedtime routine; avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed |
| Increased blood sugar | Monitor blood sugar levels; discuss with doctor; dietary adjustments |
| Muscle weakness | Gentle exercise; proper nutrition; consult doctor if severe |
Remember to report any concerning side effects to your doctor immediately. They can provide tailored advice and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Important Considerations for Children and the Elderly
Children and the elderly require special attention when taking prednisone. Dosage adjustments are frequently necessary. For children, the physician will carefully calculate the dose based on their weight and overall health. Regular monitoring of growth and development is crucial during prednisone treatment. Parents should diligently report any unusual changes to their pediatrician.
Children’s Specific Needs
Prednisone can impact a child’s bone growth, suppressing it in some cases. Regular bone density monitoring might be recommended. Close observation for signs of infection is also vital, as prednisone can weaken the immune system. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health during treatment.
Elderly Patients: Unique Challenges
Older adults often have other health conditions requiring careful medication management. Prednisone can interact with numerous medications, increasing the risk of side effects. Therefore, a thorough review of all medications is necessary before starting prednisone. The physician should closely monitor for signs of osteoporosis, increased blood sugar, and increased risk of infection. Regular blood tests will assist in assessing kidney and liver function which may be impacted by prednisone.
General Recommendations for Both Groups
Close monitoring of blood pressure, blood sugar, and weight is essential for both children and the elderly. Report any side effects, such as mood changes, increased thirst, or vision problems, to the prescribing physician immediately. A gradual tapering of the prednisone dose under medical supervision is generally recommended to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Drug Interactions: What to Avoid While on Prednisone
Prednisone interacts with many medications. Careful monitoring is crucial. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist of all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Combining prednisone with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen increases your risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Use caution, and consider alternatives if possible.
Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants)
Prednisone can affect blood clotting. If you’re on warfarin or similar medications, your doctor will need to closely monitor your INR (International Normalized Ratio) to adjust your dosage accordingly. This prevents excessive bleeding or clotting.
Potassium-Depleting Diuretics
- Prednisone can lower potassium levels. Taking potassium-wasting diuretics (like thiazide diuretics) concurrently heightens this risk.
- Your doctor might monitor your potassium levels and adjust medication accordingly.
Diabetes Medications
Prednisone can raise blood sugar levels, potentially interfering with your diabetes treatment. Your doctor may adjust your insulin or oral diabetes medications.
Vaccines
Prednisone weakens the immune system. Avoid receiving live vaccines while on prednisone, as your body may not mount an adequate immune response. Discuss this with your doctor before any vaccination.
Other Medications
- Digoxin: Prednisone might increase digoxin levels, leading to toxicity.
- Antibiotics (e.g., Rifampin): Prednisone metabolism can be affected.
- Heart Medications: Some heart medications can interact negatively with prednisone.
Herbal Supplements and Over-the-Counter Medications
Many herbal supplements and over-the-counter medications can also interact with prednisone. Always check with your doctor or pharmacist before using any new products while on this medication.
Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of stomach ulcers and other side effects associated with prednisone. Moderate alcohol intake or abstention is advisable.
Remember:
- This is not an exhaustive list.
- Consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice.
- Open communication is vital for safe medication management.
Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe and Gradual Approach
Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule. Generally, they reduce your dose by small increments, usually 2.5 mg or 5 mg every few days or weeks. Never alter your prescription without consulting your physician.
Monitoring for Side Effects
Closely monitor yourself for withdrawal symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, muscle weakness, and nausea. Report these symptoms immediately to your doctor. They might adjust the tapering schedule to minimize discomfort.
Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
Your doctor may suggest strategies to manage side effects. These might include increasing your intake of calcium and vitamin D, focusing on a healthy diet, and increasing physical activity as tolerated. Adequate rest is also vital.
Alternative Treatments
In some cases, alternative medications can help ease the transition. Discuss options like low-dose steroids or other anti-inflammatory drugs with your doctor before making any changes.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Eating nutritious foods, getting regular exercise, and managing stress are beneficial throughout the tapering process and will help support your body’s natural healing.
Staying in Touch
Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial during the tapering period. This ensures they can assess your progress, address any concerns, and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
When to Consult Your Doctor: Recognizing Warning Signs
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following:
- Severe stomach pain or persistent indigestion.
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations.
- Significant weight gain or loss (more than 5 pounds in a week).
- Increased thirst or frequent urination.
- Blurred vision.
- Swelling in your legs, ankles, or feet.
- Muscle weakness or unexplained bruising.
- Severe mood changes or depression.
- Increased susceptibility to infections.
Changes in Your Prednisone Dosage
Report any changes in your prescribed prednisone dosage to your doctor. Never adjust your medication without professional guidance.
Other Concerns
- Inform your physician about any new medications, supplements, or herbal remedies you begin taking.
- Discuss any pre-existing medical conditions or family history of health problems with your doctor.
- Keep your doctor updated on your overall health status and any changes you experience while taking prednisone.
Regular monitoring by your doctor is key for managing your prednisone treatment safely and effectively. Don’t hesitate to contact them with any concerns – your health is paramount.