Need relief from inflammation? Prednisone and naproxen are both powerful anti-inflammatories, but they work very differently. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, reduces inflammation systemically, offering rapid, potent relief for severe conditions like lupus or severe allergic reactions. However, its powerful effects come with significant side effects, including weight gain, increased blood sugar, and weakened immunity. Long-term use should always be carefully managed by a physician.
Naproxen, on the other hand, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), targets inflammation locally. It’s a common choice for milder conditions like arthritis or menstrual cramps, providing effective pain relief without the dramatic systemic impact of prednisone. While generally safer than prednisone for short-term use, naproxen can cause gastrointestinal issues, such as ulcers or bleeding, especially with prolonged use. Your doctor should be consulted about its suitability for your condition and history.
The best choice depends entirely on your specific needs and health status. For acute, severe inflammatory conditions requiring rapid, powerful relief, prednisone often provides the best option despite its potential side effects. For less severe, ongoing inflammation, naproxen may be a safer and more suitable choice, though potential gastrointestinal problems should be considered. Always discuss your options with your doctor to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual circumstances.
- Prednisone vs. Naproxen: A Detailed Comparison
- Prednisone: The Powerful Corticosteroid
- Naproxen: The NSAID for Chronic Conditions
- Prednisone: A Powerful Corticosteroid
- Naproxen: A Common NSAID
- How Naproxen Works
- Important Considerations
- Key Differences in Mechanisms of Action
- Prednisone’s Impact
- Naproxen’s Different Approach
- Clinical Implications
- Comparing Pain Relief Effectiveness
- Onset of Pain Relief
- Type of Pain Treated
- Duration of Pain Relief
- Side Effects Considerations
- Side Effects: A Head-to-Head Look
- Suitable Conditions for Each Medication
- Prednisone: When to Use It
- Naproxen: When to Use It
- When to Consult a Doctor: Considerations for Safe Use
Prednisone vs. Naproxen: A Detailed Comparison
Choose Prednisone for severe inflammation requiring rapid, powerful relief. Naproxen is better suited for milder, ongoing pain and inflammation.
Prednisone: The Powerful Corticosteroid
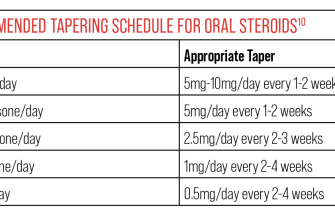
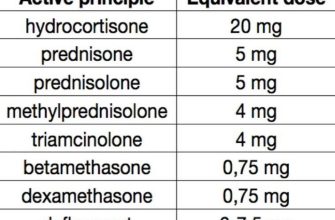
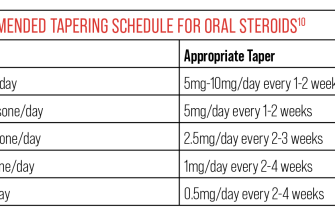
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, dramatically reduces inflammation by suppressing your immune system. This makes it highly effective for conditions like severe rheumatoid arthritis flares or allergic reactions. However, its potency comes with significant side effects, including weight gain, increased blood sugar, and increased risk of infections. Long-term use demands careful monitoring by a doctor. Expect quick results, but also potential serious long-term consequences with prolonged use.
Naproxen: The NSAID for Chronic Conditions
Naproxen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), works by reducing the production of prostaglandins, chemicals that cause pain and inflammation. It’s frequently prescribed for osteoarthritis, menstrual cramps, and other conditions causing persistent pain. While generally well-tolerated, it can still cause gastrointestinal issues such as upset stomach or ulcers. Remember to take it with food to minimize these risks. It provides less potent, but safer long-term inflammation management compared to Prednisone.
Key Differences Summarized:
Prednisone: Strong, fast-acting anti-inflammatory; significant side effects; short-term use preferred.
Naproxen: Milder anti-inflammatory; fewer severe side effects; suitable for long-term use.
Consult your doctor to determine the best medication for your specific needs. They will consider your health history and the severity of your condition before making a recommendation.
Prednisone: A Powerful Corticosteroid
Prednisone belongs to a class of drugs called corticosteroids. It powerfully reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system. Doctors prescribe it for various conditions, including severe allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, and some cancers.
Its anti-inflammatory action is significantly stronger than that of naproxen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). This makes it a go-to treatment for severe inflammation, where NSAIDs might prove insufficient.
However, this potent effect comes with potential side effects. Long-term use can lead to increased risk of osteoporosis, cataracts, high blood pressure, and increased blood sugar. Weight gain and mood changes are also common.
| Side Effect | Frequency | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Weight gain | Common | Healthy diet, exercise |
| Osteoporosis | Possible with long-term use | Calcium and Vitamin D supplements |
| High blood pressure | Possible | Monitoring and medication adjustments |
| Cataracts | Possible with long-term use | Regular eye exams |
Doctors carefully monitor patients on prednisone, gradually reducing the dosage when possible to minimize side effects. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and report any concerning symptoms immediately.
Prednisone is not a long-term solution for most conditions. Its use is typically short-term for flare-ups or in specific circumstances. Your doctor will determine the appropriate course of treatment based on your individual needs.
Naproxen: A Common NSAID
Naproxen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) widely used to treat pain and inflammation. It’s available over-the-counter (OTC) in lower doses for mild to moderate pain relief, such as headaches, menstrual cramps, and muscle aches. Higher doses require a prescription and are used for conditions like arthritis.
How Naproxen Works
Naproxen reduces pain and inflammation by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, chemicals in the body that contribute to pain and swelling. This mechanism differs from prednisone, a corticosteroid that works through a different pathway, affecting various inflammatory processes throughout the body. Naproxen’s effects are more targeted to the site of pain and inflammation.
Important Considerations
While generally safe for short-term use, long-term naproxen use carries risks including stomach ulcers, kidney problems, and cardiovascular issues. Individuals with a history of stomach ulcers, heart problems, or kidney disease should discuss naproxen use with their doctor. Like all NSAIDs, naproxen can interact with other medications, so always inform your doctor or pharmacist of all medications you are taking. Always follow the recommended dosage; exceeding the recommended dose won’t necessarily provide better pain relief but increases the risk of side effects.
Key Differences in Mechanisms of Action
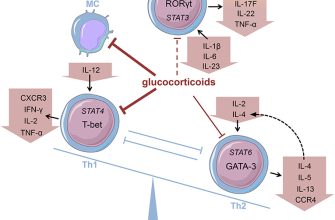
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation by suppressing the immune system. It acts by binding to intracellular receptors, influencing gene expression and decreasing the production of inflammatory mediators like cytokines. This broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory effect makes it effective for various conditions, but also increases the risk of side effects.
Prednisone’s Impact
Specifically, prednisone inhibits phospholipase A2, a key enzyme in the inflammatory cascade. This action reduces the formation of arachidonic acid, a precursor to prostaglandins and leukotrienes–powerful inflammatory molecules. The drug also stabilizes lysosomal membranes, preventing the release of damaging enzymes.
Naproxen’s Different Approach
Naproxen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), works differently. It selectively inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, specifically COX-1 and COX-2. COX enzymes are responsible for producing prostaglandins, which contribute to pain, fever, and inflammation. By blocking COX enzymes, naproxen reduces prostaglandin production, thus alleviating these symptoms.
Clinical Implications
This difference in mechanisms means that prednisone exerts a much broader, systemic anti-inflammatory effect than naproxen. Naproxen’s impact is more targeted, primarily affecting prostaglandin production at the site of inflammation. Consequently, naproxen carries a lower risk of systemic side effects, but may be less potent in treating severe inflammation.
Comparing Pain Relief Effectiveness
Prednisone and naproxen treat pain differently. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, reduces inflammation, thus lessening pain indirectly. Naproxen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), directly inhibits enzymes causing inflammation and pain. This difference affects how quickly you feel relief.
Onset of Pain Relief
Naproxen typically provides faster pain relief than prednisone. You might experience pain reduction within an hour or two of taking naproxen, depending on the dosage and your individual response. Prednisone’s impact on pain is usually more gradual, often taking several days to become noticeable, as it needs to reduce underlying inflammation first.
Type of Pain Treated
Naproxen is generally better for managing acute pain like headaches or menstrual cramps. Prednisone is more frequently used for inflammatory conditions causing severe pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis or severe allergic reactions, due to its potent anti-inflammatory action. It’s not suitable for everyday aches. Dosage and duration of treatment also play a significant role. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Duration of Pain Relief
Naproxen’s pain-relieving effects are typically shorter-lived than prednisone’s. While naproxen may provide relief for several hours, prednisone’s anti-inflammatory impact can provide longer-lasting pain reduction, depending on the condition. However, long-term prednisone use carries risks, therefore, consult a medical professional for appropriate treatment duration.
Side Effects Considerations
Both medications have potential side effects. Naproxen can cause stomach upset and increased risk of bleeding. Prednisone can lead to weight gain, mood changes, and increased blood sugar. The choice between them requires careful consideration of your individual health and the specific pain you experience. Your doctor should guide you on the best option based on your situation.
Side Effects: A Head-to-Head Look
Prednisone and naproxen cause different side effects, impacting various body systems. Naproxen, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), commonly causes gastrointestinal issues like stomach upset, heartburn, and ulcers. It may also increase the risk of bleeding, particularly in individuals with existing conditions. Kidney problems are another potential concern.
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, carries a broader range of potential side effects due to its systemic impact. Weight gain, increased blood sugar, and mood changes are frequent. Prolonged use can lead to more severe complications, including osteoporosis, cataracts, and increased susceptibility to infections. Always discuss the risks with your doctor, especially with pre-existing health conditions.
Key Differences: Naproxen’s side effects primarily affect the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys. Prednisone’s side effects are more widespread, impacting metabolism, mood, and bone health.
Recommendation: Carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks of each medication, considering your individual health status and the severity of your condition. Open communication with your doctor is paramount for managing potential side effects and ensuring the safest treatment approach. Regular monitoring is also recommended when taking either medication.
Suitable Conditions for Each Medication
Prednisone and naproxen treat different types of inflammation and pain. Choosing the right one depends entirely on your specific condition.
Prednisone: When to Use It
- Autoimmune diseases: Prednisone powerfully suppresses the immune system, making it effective for conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Severe allergic reactions: In cases of anaphylaxis or severe asthma attacks, prednisone rapidly reduces inflammation.
- Certain cancers: Prednisone is sometimes used alongside chemotherapy to manage symptoms and reduce swelling.
- Organ transplant rejection: It helps prevent the body from rejecting a transplanted organ.
- Severe inflammatory conditions: Conditions like severe bronchitis or pneumonia may benefit from prednisone’s anti-inflammatory effects.
Naproxen: When to Use It
- Osteoarthritis: Naproxen reduces pain and inflammation associated with joint degeneration.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: While not as potent as prednisone, naproxen can manage symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, often used in conjunction with other treatments.
- Menstrual cramps: Naproxen effectively relieves pain and inflammation caused by menstruation.
- Minor injuries: Naproxen helps manage pain and swelling from sprains, strains, and minor trauma.
- Dental pain and headaches: It can provide relief from mild to moderate pain.
Important Note: This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any medication, including prednisone and naproxen, to determine the most suitable treatment for your specific health needs and to discuss potential side effects.
When to Consult a Doctor: Considerations for Safe Use
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe stomach pain, vomiting blood, or black, tarry stools. These could indicate serious gastrointestinal bleeding, a potential side effect of both prednisone and naproxen.
Seek medical attention if you notice any signs of infection, such as high fever, chills, or persistent sore throat. Prednisone can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible.
- For Prednisone: Report any new or worsening muscle weakness, bone pain, or easy bruising. These could be signs of steroid-induced muscle loss or bone thinning.
- For Naproxen: Monitor for any signs of allergic reaction, including skin rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Stop taking the medication and seek immediate medical help.
Regularly monitor blood pressure and blood sugar levels, especially when using prednisone. Prednisone can increase blood pressure and blood sugar.
- Discuss with your doctor any pre-existing conditions, such as heart disease, kidney disease, or liver disease, before starting either medication.
- Inform your doctor about all other medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential interactions.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Never alter your prescribed dose without consulting your physician.
If you experience any unexpected or concerning side effects, even minor ones, contact your doctor. Early intervention can prevent complications.