Prednisone 80 mg is a high dose. This dosage is usually reserved for severe inflammatory conditions requiring rapid and significant immunosuppression. Expect to experience noticeable side effects, so close monitoring by your physician is paramount.
Your doctor will carefully weigh the benefits against potential risks. They’ll adjust the dosage and duration based on your individual health profile and response to treatment. Be prepared for regular blood tests to check for side effects, particularly on your kidneys, liver, and blood sugar.
Common side effects at this dosage include increased appetite, weight gain, mood swings, and fluid retention. More serious side effects, though less common, can include increased risk of infection, osteoporosis, and high blood pressure. Report any concerning symptoms immediately to your doctor.
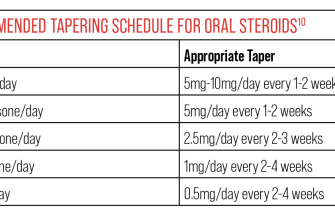
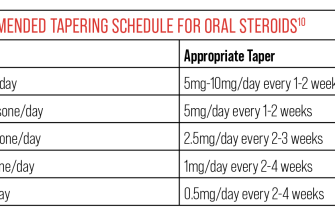
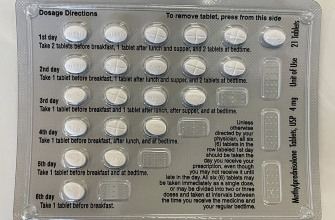
Never stop taking Prednisone 80 mg abruptly. Tapering the dose under medical supervision is crucial to prevent withdrawal symptoms and ensure your body adjusts gradually. Your doctor will create a specific tapering schedule tailored to your individual needs. Strict adherence to their instructions is extremely important for your safety and well-being.
This information is for guidance only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting, changing, or stopping any medication, including Prednisone.
- Prednisone 80 mg: Understanding the High Dose
- Common Conditions Treated with 80mg Prednisone
- Potential Side Effects of 80mg Prednisone
- Metabolic Changes
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Important Considerations and Tapering Off Prednisone
- Monitoring for Side Effects
- Tapering Schedule: A Gradual Descent
- Addressing Withdrawal Symptoms
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- Long-Term Considerations
- Communication with Your Doctor
Prednisone 80 mg: Understanding the High Dose
Prednisone 80 mg is a significantly high dose. This level is typically reserved for severe inflammatory conditions requiring rapid and potent immunosuppression. Expect potential side effects.
Common side effects at this dosage include increased appetite and weight gain, fluid retention, mood swings, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. More serious side effects, such as osteoporosis, infections, and cataracts, are also possible with prolonged use. Regular monitoring by your doctor is paramount.
Your doctor will closely monitor your blood pressure, blood sugar, and electrolyte levels. Regular blood tests are necessary to detect and manage potential complications. They’ll also assess your overall health and adjust the dosage as needed.
Gradual tapering of the dose is crucial upon completion of treatment to minimize withdrawal symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Never stop taking Prednisone suddenly without your doctor’s guidance.
Diet and lifestyle modifications can help mitigate some side effects. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can positively impact your overall health while on Prednisone.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always discuss your treatment plan and any concerns with your physician.
Common Conditions Treated with 80mg Prednisone
An 80mg daily dose of Prednisone is typically reserved for severe inflammatory conditions requiring aggressive treatment. This high dose isn’t a first-line approach; it’s usually considered when other treatments have proven insufficient.
Severe Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis or severe angioedema may necessitate this high dose to rapidly control inflammation and prevent life-threatening complications. Close medical supervision is crucial.
Acute Exacerbations of Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis) might require this dosage during periods of intense flare-ups to quell inflammation and reduce symptoms. Expect close monitoring of side effects.
Certain Cancers and Related Complications: Some cancers and their treatments (e.g., chemotherapy-induced inflammation) might necessitate this level of Prednisone to manage severe swelling, pain, or other complications. Dosage is tailored to individual needs and response.
Severe Asthma Exacerbations: Life-threatening asthma attacks requiring immediate and powerful anti-inflammatory action can benefit from this high dose. It’s usually part of a comprehensive treatment plan including other medications.
Important Note: This is not an exhaustive list. The decision to prescribe 80mg Prednisone rests solely with a physician, considering individual patient factors, disease severity, and response to treatment. Prednisone has potential side effects, and prolonged high-dose use carries significant risks. Regular monitoring is mandatory.
Potential Side Effects of 80mg Prednisone
Taking 80mg of Prednisone daily is a high dose, significantly increasing the risk of side effects. Expect potential changes in your body and mind. Monitor yourself closely and report any concerns to your doctor immediately.
Metabolic Changes
Weight gain is common due to increased appetite and fluid retention. You may also experience increased blood sugar, potentially worsening existing diabetes or causing new-onset diabetes. Elevated cholesterol and triglycerides are also possible, increasing your risk of heart disease. Maintain a healthy diet and regular exercise to mitigate these effects as much as your health allows.
Other Potential Side Effects
Mood swings, including irritability, anxiety, and even depression, are possible. Insomnia and difficulty sleeping are also frequent complaints. Prednisone can weaken bones (osteoporosis), so discuss bone density monitoring with your doctor. Increased susceptibility to infections is another significant risk. Watch for any signs of infection, like fever or unusual aches, and seek medical attention promptly if needed. You might also experience high blood pressure, muscle weakness, and thinning skin. Remember, individual reactions vary greatly.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Stomach upset, including heartburn, nausea, and ulcers, is a possibility. Taking Prednisone with food can often help reduce these issues. Consult your doctor about the possibility of taking additional medication to help protect your stomach lining.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and seek their guidance for any concerns regarding side effects.
Important Considerations and Tapering Off Prednisone
Never stop Prednisone abruptly. Sudden cessation can cause serious withdrawal symptoms.
Monitoring for Side Effects
Prednisone, especially at 80mg, carries significant side effects. Regularly monitor blood pressure, blood sugar, and weight. Report any unusual changes to your doctor immediately. Pay attention to potential mood swings and bone density issues.
- Blood pressure checks: Aim for at least weekly monitoring.
- Blood sugar testing: Frequency depends on your doctor’s recommendations; it might be daily for diabetics.
- Weight monitoring: Daily weigh-ins can help catch fluid retention early.
Tapering Schedule: A Gradual Descent
Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule. This usually involves gradually reducing your dose by small increments over weeks or months. Commonly, reductions are made every few days or weeks. Strictly adhere to this plan.
- Expect slow decreases: Rapid reduction increases the risk of severe withdrawal.
- Doctor’s guidance: Your healthcare provider will determine the best tapering rate based on your individual response and health history.
- Flexibility: If you experience severe side effects during tapering, your doctor may adjust the schedule.
Addressing Withdrawal Symptoms
Expect potential withdrawal symptoms during tapering, including fatigue, muscle weakness, and joint pain. These are often manageable with close monitoring and support from your physician.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Maintain a healthy diet: Focus on balanced meals and nutrient-rich foods.
- Prioritize regular exercise: Gentle exercise can help mitigate some side effects. Begin slowly and gradually increase intensity.
- Adequate rest: Allow your body sufficient time for recovery.
Long-Term Considerations
After completing the tapering process, continue to monitor your health closely. Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor to assess your overall well-being and manage any potential lingering side effects.
Communication with Your Doctor
Open communication with your doctor is crucial. Report any concerns or changes in your health promptly. They will provide necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.