Prednisone, taken orally, can significantly reduce hip bursitis inflammation within days. This powerful anti-inflammatory medication works by suppressing your immune system’s response, thus easing pain and improving mobility. Expect noticeable relief within 24-72 hours, though the full effect may take longer.
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on your specific condition and health history. Typical treatment involves short courses–usually lasting a few weeks, rarely longer–to minimize side effects. They’ll carefully monitor your progress and adjust the regimen as needed. Regular follow-up appointments are critical for safe and effective management.
Remember, oral prednisone isn’t a long-term solution. It addresses the immediate inflammation but doesn’t treat the underlying cause of your bursitis. Your doctor will likely recommend additional therapies like physical therapy to strengthen supporting muscles, improve range of motion, and prevent future flare-ups. They may also suggest lifestyle modifications, such as changes to your activities or footwear, to reduce strain on your hip.
Important Note: Prednisone carries potential side effects, including weight gain, increased blood sugar, and stomach upset. Discuss any concerns or pre-existing conditions with your physician before starting this medication. Promptly report any adverse effects to your doctor for appropriate management.
- Oral Prednisone for Hip Bursitis
- Dosage and Duration
- Potential Side Effects
- Alternative and Complementary Treatments
- When to See a Doctor
- Long-Term Management
- What is Hip Bursitis and How Does Prednisone Help?
- Prednisone’s Mechanism
- Important Considerations
- Dosage and Administration of Oral Prednisone for Hip Bursitis
- Typical Prednisone Regimen
- Administration Guidelines
- Important Considerations
- Monitoring and Follow-Up
- Potential Side Effects of Oral Prednisone and How to Manage Them
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Increased Blood Sugar
- Mood Changes
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Managing Side Effects: A Summary
- Contact Your Doctor
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prednisone Use for Hip Bursitis
- Alternative Treatments for Hip Bursitis Besides Prednisone
- Long-Term Outlook and Management of Hip Bursitis
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Ongoing Care
- Recurrence Prevention
Oral Prednisone for Hip Bursitis
Oral prednisone reduces inflammation, offering temporary pain relief for hip bursitis. Doctors usually prescribe a short course, typically lasting a few days to a couple of weeks, to minimize side effects.
Dosage and Duration
Your doctor determines the precise prednisone dosage based on your individual needs and the severity of your bursitis. Common starting doses range from 20-60mg daily, gradually tapering down over time to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician. Expect a noticeable decrease in pain and inflammation within a few days of starting treatment.
Potential Side Effects
While effective, prednisone can have side effects. Common ones include increased appetite, weight gain, insomnia, and mood changes. More serious, though less frequent, side effects are possible. Open communication with your doctor is critical to manage any side effects that arise.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
Prednisone is often part of a broader treatment plan. Physical therapy helps strengthen supporting muscles and improve hip mobility, lessening future bursitis flare-ups. Rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers provide additional comfort. Your doctor can help you develop a personalized treatment approach that addresses your specific needs.
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if your pain worsens despite treatment or if you experience unusual symptoms. Early intervention is key for optimal management of hip bursitis.
Long-Term Management
Long-term use of prednisone isn’t recommended for hip bursitis due to potential side effects. Focus on a holistic approach that combines medication with lifestyle modifications like maintaining a healthy weight and regular exercise to prevent future episodes. Properly addressing the root cause of the inflammation is crucial for sustainable relief.
What is Hip Bursitis and How Does Prednisone Help?
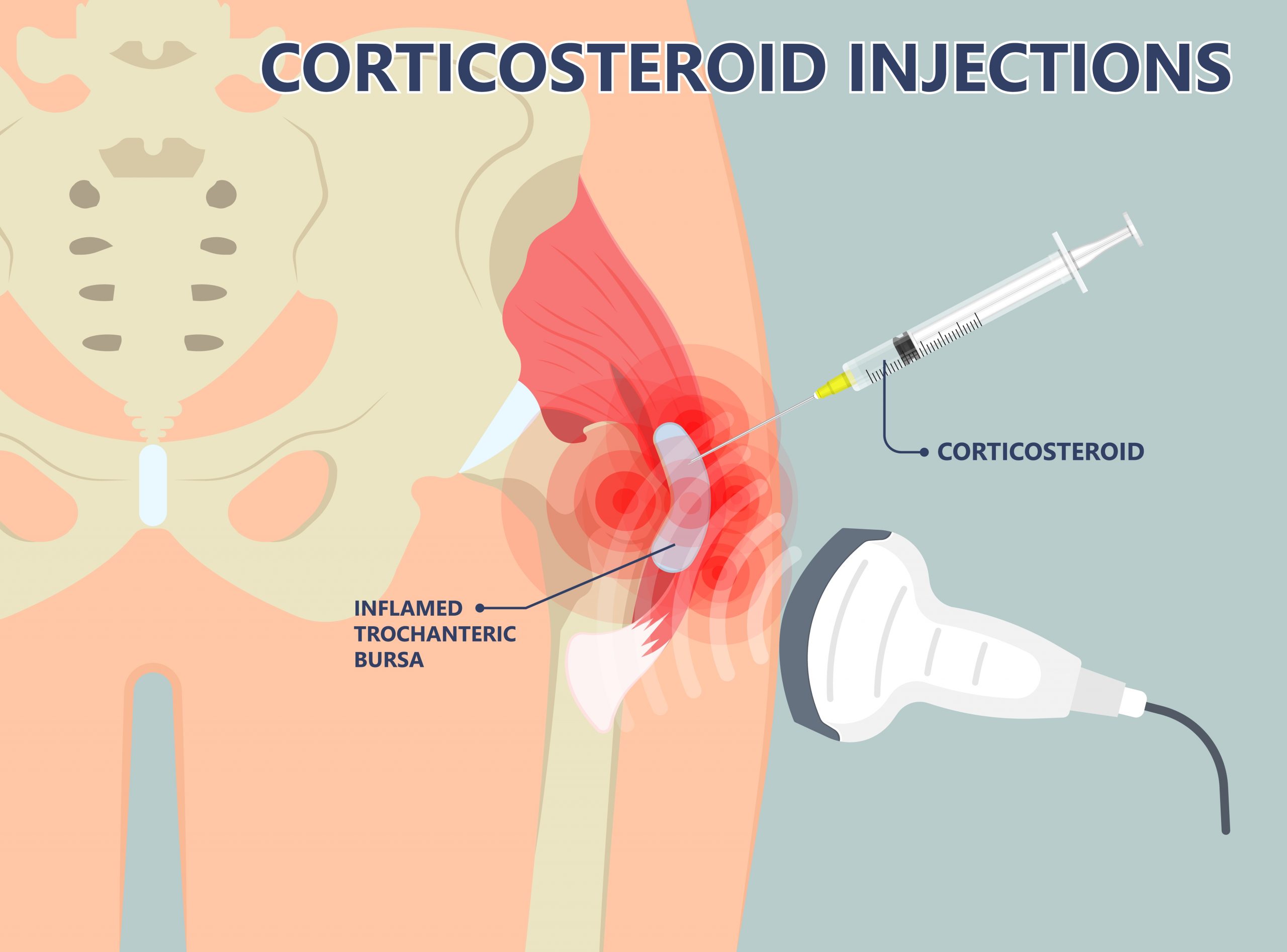
Hip bursitis is inflammation of the bursae, fluid-filled sacs cushioning your hip joint. This inflammation causes pain, particularly with movement. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, directly reduces this inflammation.
Prednisone’s Mechanism
Prednisone works by suppressing your immune system’s response, thus decreasing the swelling and pain associated with hip bursitis. It targets the inflammatory cells causing the problem, providing rapid pain relief. This allows increased range of motion and improved function.
Important Considerations
While prednisone offers quick pain relief, it’s a short-term solution. Long-term use carries risks like weakened bones and increased susceptibility to infections. Your doctor will likely prescribe it for a limited time, alongside other therapies like physical therapy, to address the underlying cause and promote long-term healing. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Side effects can include increased appetite, weight gain, and mood changes. Report any concerning symptoms promptly.
Dosage and Administration of Oral Prednisone for Hip Bursitis
Your doctor will determine the appropriate prednisone dosage based on your individual needs and the severity of your hip bursitis. Typical treatment involves a short course of medication.
Typical Prednisone Regimen
A common starting point is a relatively high dose, gradually tapered down over several days or weeks. This approach aims to quickly reduce inflammation and pain, followed by a slower decrease to minimize potential side effects.
- Example Regimen: A doctor might prescribe 40-60mg daily for the first few days, then reduce by 5-10mg every few days until the daily dose reaches zero.
- Duration: The duration of treatment varies, typically ranging from a few days to several weeks. Longer courses are less common due to the risk of side effects.
Administration Guidelines
Prednisone is usually taken orally, once or twice daily, with food to reduce stomach upset.
- Timing: Consistent timing is important for maintaining consistent blood levels. Take your dose at the same time each day.
- Food: Taking prednisone with food helps minimize gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Missed Dose: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses.
Important Considerations
Prednisone has potential side effects. Discuss these with your physician; they can help manage risks and ensure the treatment aligns with your health profile.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments allow your doctor to monitor your progress, adjust the dosage if needed, and address any side effects you may experience.
- Pain Management: Your doctor will track your pain levels to assess the treatment’s efficacy.
- Side Effect Assessment: They will also monitor for side effects such as increased blood sugar, weight gain, or mood changes.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Do not stop taking prednisone abruptly without consulting your physician; gradual tapering is crucial to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Potential Side Effects of Oral Prednisone and How to Manage Them
Prednisone can cause several side effects. Monitor yourself closely for these, and contact your doctor immediately if you experience anything concerning.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Prednisone frequently increases stomach acid, leading to heartburn, indigestion, or ulcers. To mitigate this, take prednisone with food. Your doctor might prescribe a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) like omeprazole to protect your stomach lining. Avoid alcohol and spicy foods.
Increased Blood Sugar
Prednisone elevates blood sugar levels, potentially exacerbating or causing diabetes. Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial, especially if you have diabetes or risk factors. Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise are important. Your doctor might recommend adjustments to your diabetes medication.
Mood Changes
Some people experience mood swings, anxiety, or insomnia while taking prednisone. Maintain a consistent sleep schedule, practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, and consider talking to a therapist if needed. Your doctor can help adjust your medication or suggest other coping strategies.
Other Potential Side Effects
Other potential side effects include increased risk of infection, fluid retention (causing swelling), weight gain, thinning skin, and bone thinning (osteoporosis). Maintain good hygiene to prevent infections. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient calcium and vitamin D intake can help minimize some of these risks.
Managing Side Effects: A Summary
| Side Effect | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Heartburn/Indigestion | Take prednisone with food; consider a PPI |
| High Blood Sugar | Monitor blood sugar regularly; healthy diet and exercise; medication adjustment |
| Mood Changes | Consistent sleep; relaxation techniques; therapy |
| Increased Infection Risk | Good hygiene |
| Fluid Retention/Weight Gain | Low-sodium diet; regular exercise |
| Thinning Skin/Bones | Balanced diet; calcium & vitamin D supplementation |
Contact Your Doctor
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Regular communication with your doctor is paramount for safe and effective prednisone use.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prednisone Use for Hip Bursitis
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any allergic reactions, such as hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing, after starting prednisone. This requires prompt medical attention.
Schedule a follow-up appointment if your hip pain doesn’t improve significantly after a week of prednisone treatment, or if it worsens. Your doctor can adjust your treatment plan or explore other options.
Seek medical advice if you notice any signs of infection, like increased redness, warmth, or pus around the affected area. Prednisone can suppress your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
Report any new or worsening symptoms, such as muscle weakness, stomach upset, increased thirst, or frequent urination. These could indicate side effects of prednisone that need managing.
Discuss your medication with your doctor before starting any other medications, supplements, or herbal remedies. Interactions can occur, impacting the efficacy and safety of your treatment.
Consult your doctor if you have concerns about long-term prednisone use or potential side effects. They can help you understand the risks and benefits, and develop a plan for tapering off the medication safely.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and keep them informed about your progress.
Alternative Treatments for Hip Bursitis Besides Prednisone
Consider physical therapy. A skilled therapist creates a personalized plan including exercises to strengthen hip muscles and improve flexibility, reducing pain and improving range of motion. Many find relief through targeted stretches and strengthening routines.
Try corticosteroid injections. While similar to oral prednisone, these injections deliver medication directly to the inflamed bursa, providing more targeted relief with potentially fewer systemic side effects. Discuss this option with your doctor.
Explore ice and heat therapy. Applying ice packs for 15-20 minutes several times a day can reduce inflammation. Heat therapy, such as warm showers or heating pads, can relax tight muscles and ease discomfort. Experiment to find what works best for you.
Use over-the-counter pain relievers. Ibuprofen or naproxen can effectively manage pain and inflammation. Always follow dosage instructions carefully.
Rest and modify activities. Avoid activities that aggravate your hip pain. Use assistive devices like canes if needed, to reduce stress on the joint.
Consider extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT). This non-invasive treatment uses sound waves to stimulate healing and reduce pain. It’s an option for those who haven’t found relief from other treatments. Discuss this possibility with your doctor to determine if it’s a good fit for your condition.
Explore acupuncture. Some find relief through acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. This treatment aims to stimulate healing and reduce pain.
Long-Term Outlook and Management of Hip Bursitis
Most hip bursitis cases resolve within a few weeks with conservative treatment. Pain typically subsides gradually, though some lingering discomfort is possible. Regular, low-impact exercise like swimming or cycling helps maintain hip mobility and strengthen surrounding muscles, preventing future episodes.
Lifestyle Modifications
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the hip joint. Avoid activities that aggravate your symptoms. Consider using supportive footwear and orthotics to improve posture and reduce strain. Ice application and gentle stretching can alleviate pain and stiffness.
Ongoing Care
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in long-term management. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion. They can also teach you proper techniques to avoid re-injury. Regular follow-up with your doctor helps monitor your progress and address any concerns.
Recurrence Prevention
Addressing underlying causes like poor posture or repetitive movements is key to prevention. Listen to your body; rest when needed and avoid pushing yourself too hard. Staying active with appropriate exercise helps build resilience and reduces the risk of future flare-ups.