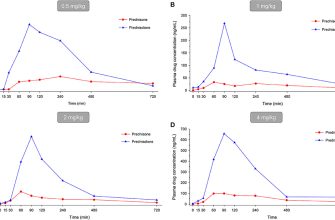
A three-month course of 15mg prednisone requires careful monitoring. This dosage is moderate, but long-term use necessitates close attention to potential side effects. Expect regular check-ups with your doctor to assess your progress and adjust the treatment plan if needed.
Prioritize a healthy diet rich in potassium and calcium to mitigate potential mineral imbalances. Prednisone can impact bone density; regular exercise and adequate vitamin D intake are crucial for bone health. Discuss potential interactions with other medications you take with your physician.
Be aware of common side effects such as weight gain, increased appetite, mood swings, and insomnia. Keeping a detailed record of your symptoms will help you and your doctor manage them effectively. Report any significant changes in your health immediately. We recommend open communication with your healthcare provider throughout the entire treatment period. Remember, proactive management yields the best results.
- 15 mg Prednisone for 3 Months: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Treatment
- Common Uses
- Important Considerations
- Managing Potential Side Effects
- Tapering Off Prednisone
- Further Information
- Potential Side Effects and Management Strategies
- Metabolic Effects
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Monitoring Your Health During Prednisone Use
- Managing Blood Sugar
- Weight Management
- Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe and Effective Approach
- Interactions with Other Medications and Lifestyle Factors
- When to Consult Your Doctor During and After Treatment
- During Treatment
- After Treatment
- Managing Side Effects
15 mg Prednisone for 3 Months: A Detailed Guide
Consult your doctor immediately for personalized advice. A three-month course of 15mg prednisone requires close monitoring due to potential side effects.
Expect potential side effects including increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. Regularly monitor these factors and report any concerns to your physician.
Your doctor will likely schedule blood tests to check for changes in your blood pressure, electrolyte levels, and blood glucose. Follow their instructions precisely regarding testing frequency.
Gradual tapering of the prednisone dosage is crucial to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Never stop taking prednisone abruptly. Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule. Strictly adhere to it.
| Potential Side Effect | Management Strategy |
|---|---|
| Weight gain | Maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly. Discuss dietary modifications with your doctor or a registered dietitian. |
| Mood changes | Communicate openly with your doctor and support network. Consider stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga. |
| Insomnia | Maintain a regular sleep schedule. Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Discuss sleep aids with your doctor if needed. |
| Increased blood sugar | Monitor blood sugar levels regularly. Adjust your diet and/or medication as directed by your doctor. |
Maintain open communication with your doctor throughout the treatment. Report any new or worsening symptoms immediately. Regular follow-up appointments are critical for monitoring your progress and adjusting treatment as necessary. This detailed guide provides information but is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Treatment
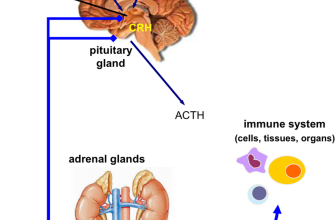
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation. Your doctor prescribed 15mg for three months likely to manage a specific inflammatory condition. This dosage and duration are typical for several inflammatory diseases but are individualized depending on your specific needs and the severity of your condition.
Common Uses
- Autoimmune Diseases: Prednisone suppresses the immune system, easing symptoms in conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Allergic Reactions: It can significantly reduce swelling and inflammation associated with severe allergies.
- Asthma: Prednisone can provide rapid relief from severe asthma attacks by reducing airway inflammation.
- Certain Cancers: In some cases, it’s used to reduce tumor size or manage related symptoms.
Important Considerations
Remember: Prednisone is a powerful medication with potential side effects. Open communication with your doctor is key. They will monitor you for any adverse reactions and adjust your dosage accordingly.
Managing Potential Side Effects
- Weight Gain: Monitor your diet and engage in regular physical activity to mitigate weight gain.
- Increased Blood Sugar: Regular blood sugar checks are crucial, particularly if you have diabetes or risk factors.
- Mood Changes: Be mindful of changes in mood and seek support if needed. Discuss this with your doctor.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Practice good hygiene and report any signs of infection immediately.
- Osteoporosis Risk: Discuss bone health with your doctor, potentially incorporating calcium and vitamin D supplements.
Tapering Off Prednisone
Never stop taking prednisone suddenly. Your doctor will create a tapering schedule to gradually reduce your dosage. This prevents withdrawal symptoms and allows your body to adjust naturally. Following this schedule meticulously is crucial for successful treatment and minimizing potential adverse effects.
Further Information
This information should not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance regarding prednisone treatment.
Potential Side Effects and Management Strategies
Prednisone, at 15mg for three months, can cause various side effects. Weight gain is common; monitor your diet and increase physical activity to mitigate this. Increased appetite often accompanies this, so mindful eating is key. Fluid retention can also occur; reducing sodium intake helps.
Metabolic Effects
Increased blood sugar is possible, especially if you have pre-existing diabetes. Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial. Your doctor might adjust your diabetes medication accordingly. High blood pressure can also develop; regular checks are recommended, and lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise are beneficial. Increased cholesterol levels are another possibility; your doctor may suggest blood lipid tests and lifestyle changes.
Other Potential Side Effects
Mood changes, including irritability or anxiety, are possible. Open communication with your doctor and support system is beneficial. Insomnia can occur; maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and avoiding caffeine before bed can help. Muscle weakness and thinning of the bones (osteoporosis) are long-term risks; regular exercise and a calcium-rich diet, along with potential supplements, are important preventative measures. Increased risk of infections necessitates cautious hygiene and prompt attention to any symptoms.
Remember to report any concerning side effects to your doctor immediately. They can adjust your medication or recommend additional strategies for managing these effects.
Monitoring Your Health During Prednisone Use
Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor. These appointments allow for consistent monitoring of your blood pressure, blood sugar, and weight. Your doctor will adjust your prednisone dosage as needed based on these readings and your overall health.
Closely monitor your blood pressure at home. Use a home blood pressure monitor and record your readings daily, ideally at the same time each day. Report any significant changes to your doctor immediately. High blood pressure is a common side effect of prednisone.
Managing Blood Sugar
If you have diabetes or are at risk of developing diabetes, monitor your blood sugar levels frequently. Prednisone can elevate blood sugar. Consult your doctor about adjusting your diabetes medication if necessary. Regular blood glucose testing is vital.
Weight Management
Weigh yourself weekly. Prednisone can cause weight gain, often due to fluid retention and increased appetite. Discuss healthy eating habits and exercise strategies with your doctor or a registered dietitian to mitigate this side effect.
Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor promptly. This includes muscle weakness, bone pain, skin changes, mood swings, or difficulty sleeping. Early detection allows for timely intervention and management of potential complications.
Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe and Effective Approach
Gradually reduce your prednisone dosage under your doctor’s supervision. A common tapering schedule involves decreasing the dose by 5mg every few days to a week, depending on your response and the doctor’s recommendations. Never abruptly stop taking prednisone.
Monitor for withdrawal symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, joint pain, or nausea. These symptoms are often manageable with careful tapering and may necessitate a slower reduction in dosage. Report any concerning symptoms to your physician immediately.
Your doctor might adjust the tapering schedule based on your individual needs and symptoms. They may prescribe other medications to mitigate withdrawal effects, such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs. Regular blood tests can help track your progress and ensure your body adapts appropriately.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle during the tapering process. Prioritize proper nutrition, regular exercise (as tolerated), and sufficient sleep. These lifestyle factors positively contribute to your overall well-being and can help manage withdrawal symptoms.
Be patient and maintain open communication with your doctor throughout the entire process. Regular check-ups are crucial to monitor your progress, make necessary adjustments, and address any emerging concerns promptly.
Complete withdrawal should be done under medical supervision. Your doctor will determine when it’s safe to completely stop taking prednisone based on your individual health and response to treatment.
Interactions with Other Medications and Lifestyle Factors
Always inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Prednisone can interact with many medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or causing side effects. For example, it can increase blood sugar levels, impacting the management of diabetes. Concurrent use with blood thinners might increase bleeding risk. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) used alongside prednisone raise the stomach ulcer risk.
Your diet plays a role. A high-sodium diet can worsen fluid retention, a potential side effect of prednisone. Conversely, a diet rich in potassium can help counter some electrolyte imbalances. Maintain a balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Alcohol consumption should be limited or avoided entirely. Prednisone can increase the risk of stomach irritation and liver problems, and alcohol exacerbates these risks. Regular exercise is generally beneficial, but consult your doctor before starting or changing your exercise routine, especially if you experience muscle weakness or other side effects from the medication.
Sufficient sleep is crucial for overall well-being and can help mitigate some prednisone side effects such as fatigue. Aim for at least 7-8 hours of quality sleep nightly. Smoking significantly increases the risk of side effects, particularly on the cardiovascular system; quitting is highly recommended. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar is necessary during prednisone treatment.
When to Consult Your Doctor During and After Treatment
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe side effects. This includes, but isn’t limited to, severe abdominal pain, vision changes, significant mood swings, or difficulty breathing.
During Treatment
- Schedule regular check-ups as advised by your doctor. These appointments allow monitoring of blood pressure, blood sugar, and other vital signs.
- Report any new or worsening symptoms, regardless of how minor they may seem. Examples include increased thirst, unexplained weight changes, or skin changes.
- Discuss any medication interactions with your doctor before taking other medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Monitor your bone health through regular assessments, if prescribed, due to potential side effects of long-term prednisone use.
After Treatment
- Follow your doctor’s instructions for gradually tapering off prednisone to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Sudden cessation can be dangerous.
- Attend follow-up appointments to assess your overall health and monitor for lingering side effects. Your doctor might order blood tests.
- Report any persistent symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, or changes in appetite after the medication is stopped.
- Pay close attention to your body’s response. If something feels amiss, don’t hesitate to contact your physician.
Managing Side Effects
Your doctor can provide strategies for managing potential side effects. This might involve lifestyle changes, adjustments to your medication, or additional support.